STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit
Serum-free differentiation kit for generating astrocyte precursors from hPSC-derived neural progenitor cells
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
-
 STEMdiff™ Neural Rosette Selection Reagent
STEMdiff™ Neural Rosette Selection ReagentEnzyme-free reagent for the selective detachment of neural rosettes
-
 STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction Kit
STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction KitSerum-free medium kit for highly efficient SMAD inhibition-mediated neural induction of human ES and iPS cells
-
 STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation Kit
STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation KitMaturation kit for the generation of cortical-type astrocytes from human ES and iPS cell-derived astrocyte precursors
-
 Human iPSC-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells
Human iPSC-Derived Neural Progenitor CellsFrozen human neural progenitor cells differentiated from the human induced pluripotent stem cell line, SCTi003-A
-
 DMEM/F-12 with 15 mM HEPES
DMEM/F-12 with 15 mM HEPESDulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium/Nutrient Ham's Mixture F-12 (DMEM/F-12) with 15 mM HEPES buffer
-
Labeling Antibodies
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
Overview
Data Figures
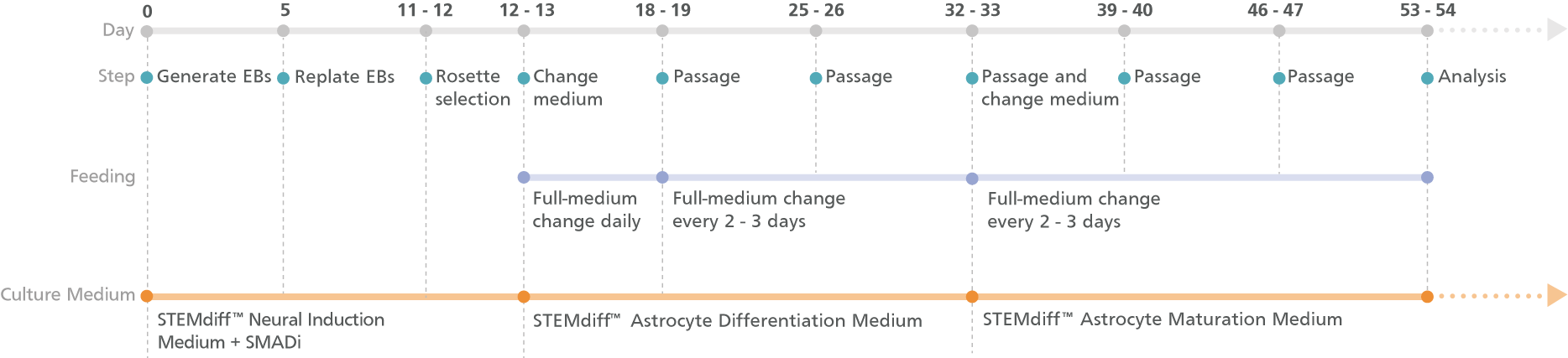
Figure 1. Schematic for the Embryoid Body Protocol
Cortical-type astrocyte precursors can be generated in 20 days from hPSC-derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs) after selecting neural rosettes from replated embryoid bodies. For the maturation of precursors to cortical-type astrocytes, see the PIS.
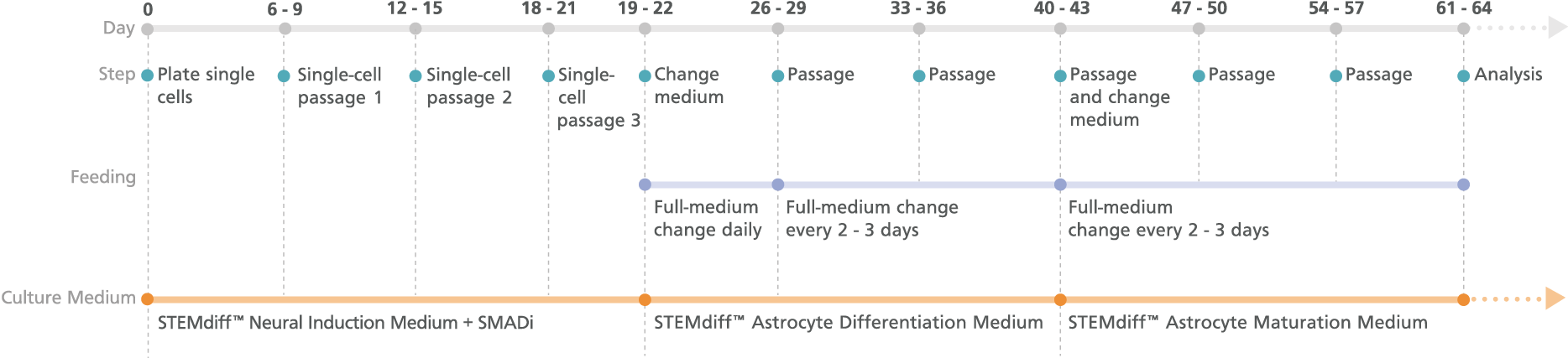
Figure 2. Schematic for the Monolayer Protocol
Cortical-type astrocyte precursors can be generated in 21 days from neural progenitor cell (NPC) monolayers derived from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells after three single-cell passages. For the maturation of precursors to cortical-type astrocytes, see the PIS.

Figure 3. Cortical-Type Astrocytes Are Generated After Culture in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits
NPCs generated from hPSCs in TeSR™-E8™ using the STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction Kit embryoid body (EB) protocol were differentiated and matured to cortical-type astrocytes using the STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. Cortical-type astrocytes were formed after iPS cell-derived NPCs were cultured with the STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit for 3 weeks and STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation Kit for 3 weeks. (A) Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (gray). The resulting cultures contain a highly pure population of astrocytes, which are (B) more than 60% GFAP-positive (green) and (C) more than 70% S100B-positive (magenta), with (D) fewer than 15% neurons (DCX-positive cells, cyan). Scale bar = 100 μm.

Figure 4. STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Kits Generate Cells Expressing Expected Levels of Genes Characteristic for Astrocytes
Embryonic stem and induced pluripotent stem cells from a variety of lines (n = 6, maintained in mTeSR™1 or TeSR™-E8™) were differentiated to NPCs using the STEMdiff™ SMADi Neural Induction Kit embryoid body protocol. Cells were then grown in STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit for 3 weeks followed by STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Maturation Kit for 3 weeks prior to analysis. Expression levels were measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and normalized to hPSC controls relative to housekeeping genes 18S and TBP.

Figure 5. PSC-Derived Astrocytes and Neurons Can Be Co-Cultured to Model Cell-Cell Interactions In Vitro
NPCs generated from the H1 cell line were differentiated to astrocytes using STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. H9 cell-derived NPCs were differentiated to forebrain-type neurons using STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Differentiation and Maturation Kits. For co-culture, matured astrocytes were seeded onto forebrain neurons that had been in STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium for at least one week. Co-cultures were then switched to STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium the following day and for the remaining co-culture. (A) Neurons cultured alone, following the co-culture feeding schedule, are labeled with DCX (green). (B) DCX-positive neurons (green) and astrocytes (GFAP, red) can be co-cultured for at least 1 - 2 weeks prior to analysis. For a detailed co-culture protocol, please see the Methods Library.

Figure 6. PSC-Derived Neurons Survive and Mature when Co-Cultured with PSC-Derived Astrocytes
NPCs generated from the STiPS-R038 cell line were differentiated to astrocytes using STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation and Maturation Kits. STiPS-M001 cell-derived NPCs were differentiated to forebrain-type neurons using STEMdiff™ Forebrain Neuron Differentiation and Maturation Kits. After co-culture for one week, neurons (A) had significantly increased neurite outgrowth as measured on MAP2-positive neurons with the NeuriteTracer plugin for ImageJ (M Pool et al. J Neurosci Methods, 2008) and (B) were more numerous than neurons cultured alone using the same feeding schedule. *, p < 0.05
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (22)
Related Products
-
 NeuroCult™ SM1 Neuronal Supplement
NeuroCult™ SM1 Neuronal SupplementSupplement (50X) for the serum-free culture of neurons
-
 BrainPhys™ Neuronal Medium
BrainPhys™ Neuronal MediumSerum-free neurophysiological basal medium for improved neuronal function
-
 N2 Supplement-A
N2 Supplement-AFor neural and pancreatic differentiation of mouse and human ES and iPS cells
-
 Anti-Beta-Tubulin III Antibody, Clone TUJ1
Anti-Beta-Tubulin III Antibody, Clone TUJ1Mouse monoclonal IgG2a antibody against human, mouse, rat betatubulin III
Item added to your cart

STEMdiff™ Astrocyte Differentiation Kit
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.






















