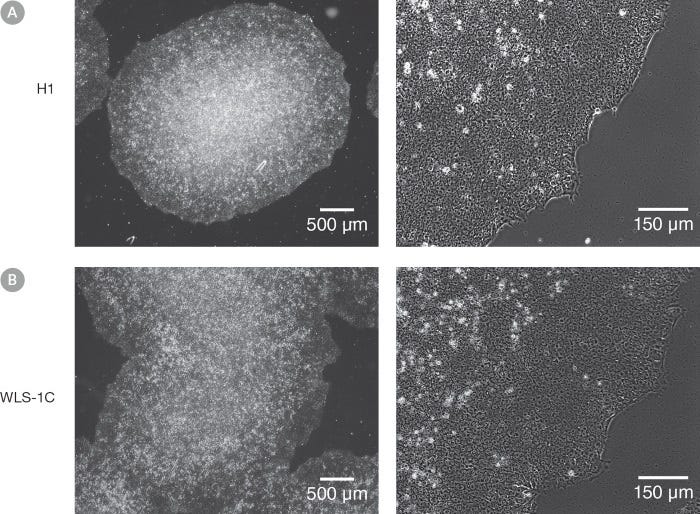
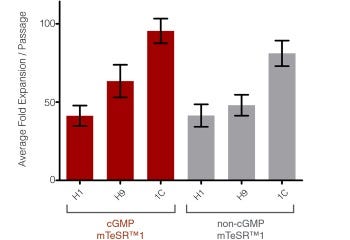
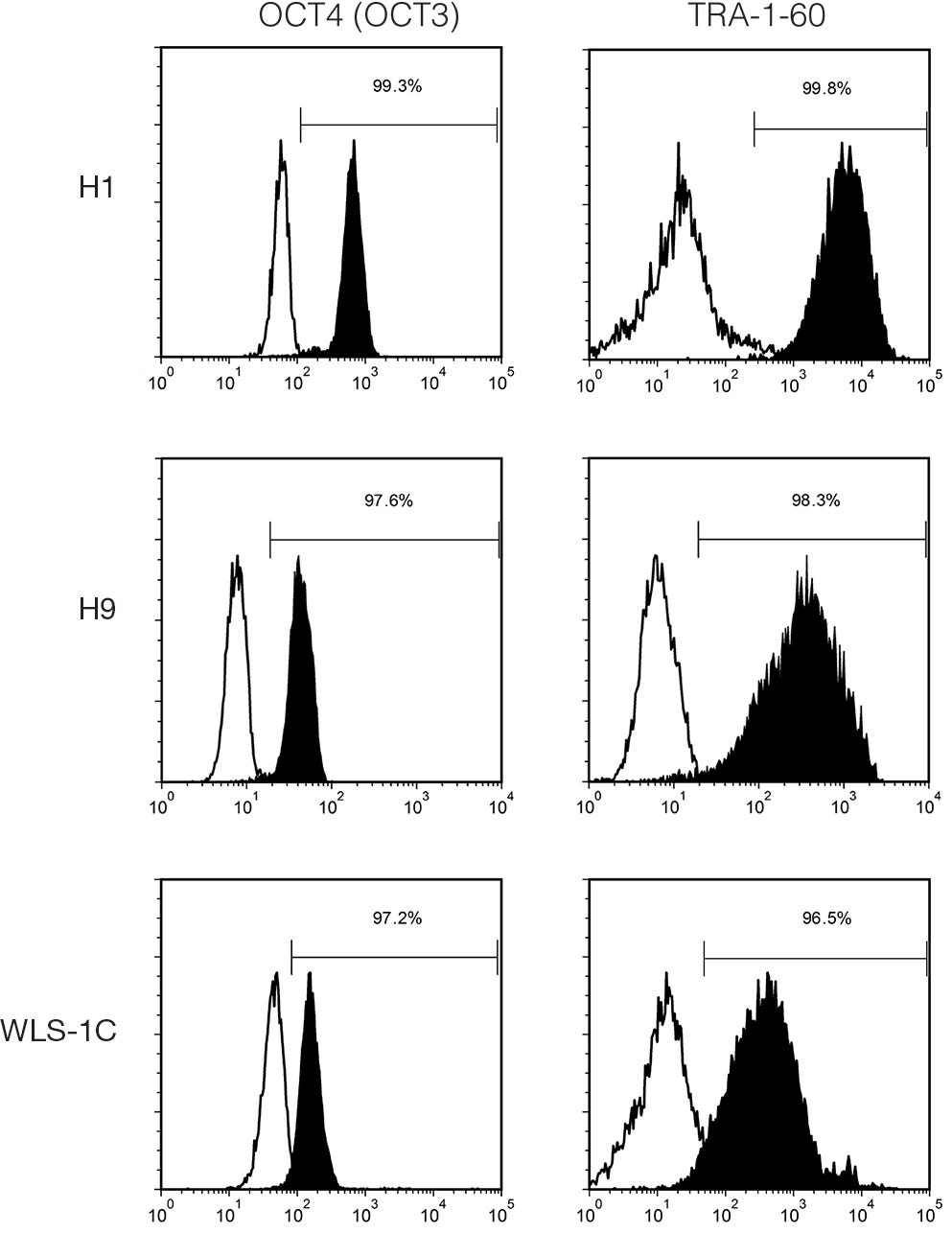
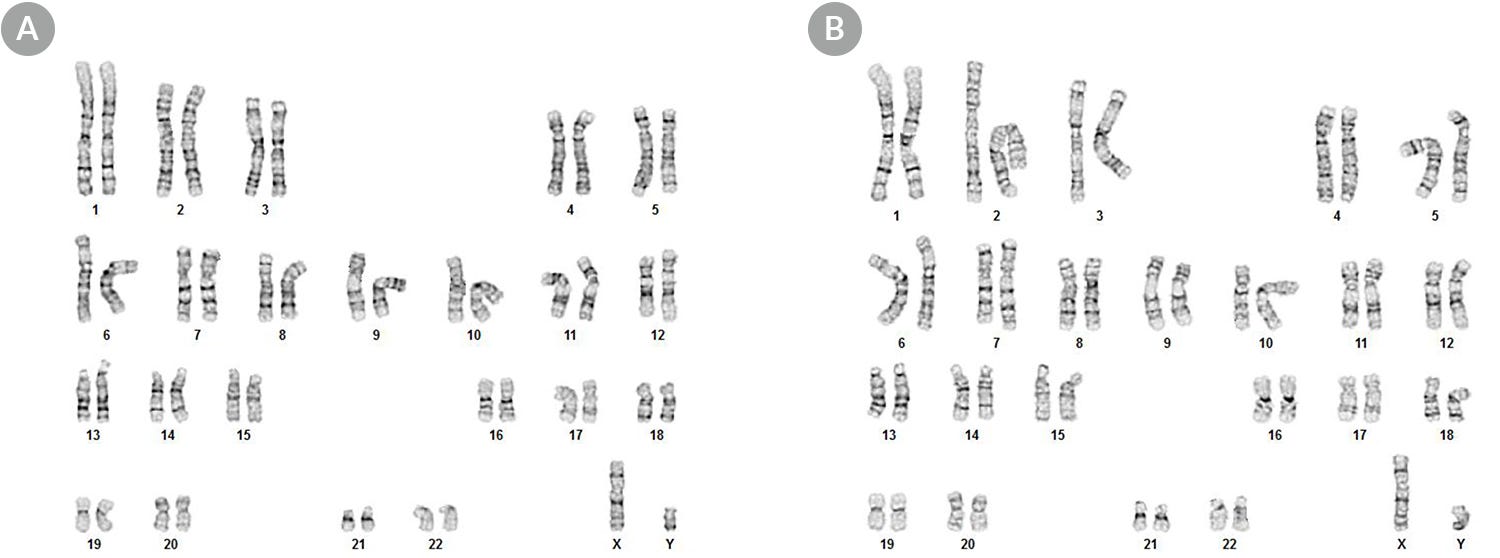
mTeSR™1
cGMP, feeder-free maintenance medium for human ES and iPS cells

Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
Overview
Data Figures
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (41)
Publications (1585)
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
This product was developed under license to intellectual property owned by WiCell™ Research Institute. This product is sold for research use only (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity) under a non-transferable, limited-use license. Purchase of this product does not include the right to sell, use or otherwise transfer this product for commercial purposes (i.e., any activity undertaken for consideration, such as use of this product for manufacturing, or resale of this product or any materials made using this product, or use of this product or any materials made using this product to provide services) or clinical use (i.e., administration of this product or any material using this product to humans) or the right to implant any material made using this product into an animal by, or in collaboration with, a for-profit entity, for purposes other than basic pre-clinical research applications (including without limitation teratoma assays) to validate the function of the cells. Purchasers who do not agree to the terms and conditions set forth above should return the product in acceptable conditions to the seller for a refund.
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.