StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Supplement (100X)
Supplement for the differentiation of lymphoid progenitors to NK cells
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
-
 StemSpan™ SFEM II
StemSpan™ SFEM IISerum-free medium for culture and expansion of hematopoietic cells
-
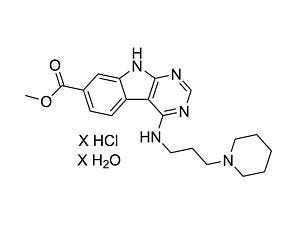 UM729
UM729Pyrimido-indole derivative that enhances HSC self-renewal in vitro
-
Labeling Antibodies
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
Overview
For your convenience, the supplement is available either individually or as part of the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit or the STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit. Lymphoid progenitor cells generated by differentiation of CD34+ cells in StemSpan™ SFEM II medium containing StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Supplement (10X) on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material (100X) can be further differentiated to NK cells using this supplement.
The StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Supplement (100X) is intended to be used in combination with StemSpan™ SFEM II and UM729 to promote differentiation into CD56+ NK cells.
For detailed information on protocols for NK cell generation, please explore the Technical Manual.
Data Figures
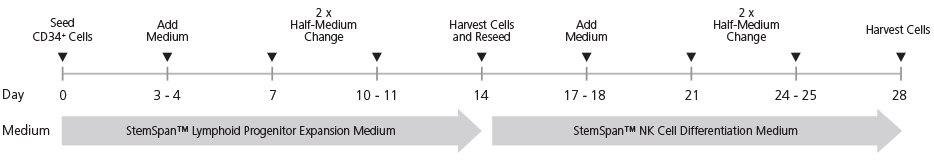
Figure 1. StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Protocol
CB-derived CD34+ cells are seeded on day 0. Medium should be topped up after 3 - 4 days of culture followed by two half-medium changes every 3 - 4 days. On day 14, cells at the lymphoid progenitor stage are harvested and reseeded for further differentiation into NK cells. Top-up and half-medium changes should be performed every 3 - 4 days after harvest and reseed, as indicated in the figure. Note: UM729 should only be added to the NK Cell Differentiation Medium, but not the Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium.
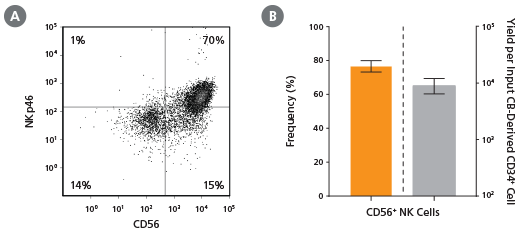
Figure 2. Frequency and Yield of CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
CB-derived CD34+ cells (freshly isolated or frozen) were cultured with the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit for 28 days as described. Cells were harvested and analyzed for (A,B) CD56 and (A) NKp46 expression by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and viability staining. (B) The average frequency of viable CD56+ NK cells on day 28 was 77%, with ~9,000 CD56+ cells produced per input CB-derived CD34+ cell. Shown are means with 95% confidence intervals (n = 45: 23 freshly isolated and 22 frozen CD34+ cell samples). BM-derived CD34+ cells were also differentiated into NK cells using the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit. The yield of NK cells from BM HSPCs is typically lower than with CB, averaging ~75 per input CD34+ cell (n = 3, data not shown).
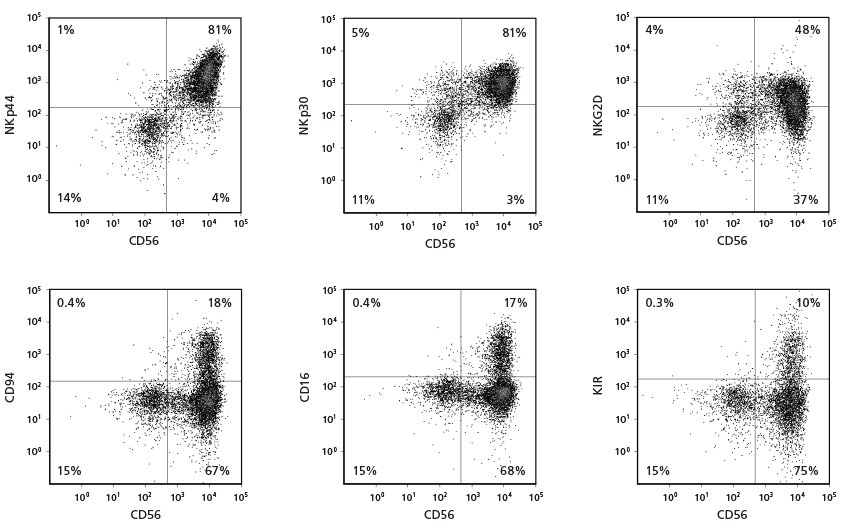
Figure 3. Cell Surface Marker Expression on CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
CB-derived CD34+ cells were cultured with the StemSpan™ NK Cell Generation Kit for 28 days. The differentiated cells were harvested and analysed by flow cytometry for the expression of CD56, NKp44, NKp30, NKG2D, CD94, CD16, and KIR. Staining for KIR molecules was performed using a combination of two clones for the antibody, 180704 and HP-MA4, as each recognizes a distinct subset of KIR molecules.
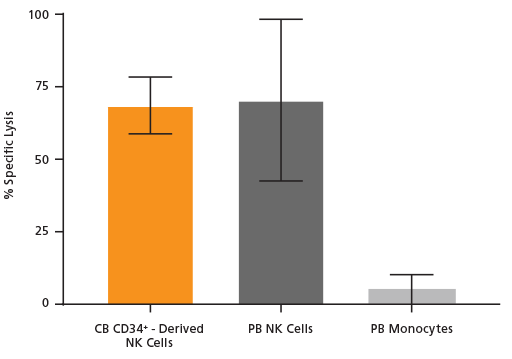
Figure 4. Cultured NK Cells Exhibit Cytotoxicity Toward K562 Cell Line
NK cells were generated from CB-derived CD34+ cells over 28 days using the protocol in Figure 1. On day 28, cells were harvested, stained for CD56, and viable CD56+ cells were counted. K562 cells were incubated with 8 μM calcein AM at 37°C for 1 hour and then washed twice. CD56+ NK cells were then combined with 10,000 of these calcein AM-labeled K562 target cells at an Effector:Target ratio of 5:1 in U-bottom 96-well plates and co-cultured at 37°C for 4 hours. Adult peripheral blood (PB) NK cells and monocytes isolated using EasySep™ were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. PB NK cells were cultured overnight with the NK Cell Differentiation Supplement and SFEM II, while PB monocytes were cultured overnight in SFEM II only. To detect spontaneous release, control wells containing only calcein AM-labeled K562 target cells were set up. The labeled K562 cells were treated with 1% Triton™ X-100 to measure maximum release. After incubation, plates were centrifuged at 500 x g for 5 minutes and 100 μL of supernatant was transferred to black plates and analyzed using a SpectraMax® microplate reader (excitation 485 nm/emission 530 nm). Results are expressed as % specific lysis: [(test release - spontaneous release) x 100] / (maximum release - spontaneous release). CB CD34+-derived NK cells show similar killing activity toward K562 target cells compared to PB NK cells. Shown are means ± SD (CB CD34+-derived NK cells: n = 18, PB NK cells and monocytes: n = 7).
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (4)
Related Products
-
 StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Sup...
StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Sup...Supplement for the expansion and differentiation of human CD34+ cells to lymphoid progenitor cells
-
 StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating ...
StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating ...Coating material for the expansion and differentiation of lymphoid cells
-
 EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Sel...
EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Sel...Immunomagnetic positive selection of human CD34+ cells from cord blood
-
 Anti-Human CD56 Antibody, Clone HCD56
Anti-Human CD56 Antibody, Clone HCD56Mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody against human CD56 (NCAM)
-
 Human Cord Blood CD34+ Cells, Frozen
Human Cord Blood CD34+ Cells, FrozenPrimary human cells, frozen
Item added to your cart

StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Supplement (100X)
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.





