EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent
Immunomagnetic negative selection
Overview
This product replaces the EasySep™ Human Glycophorin A Depletion Kit (Catalog #18352) for even faster cell isolations.
Data Figures

Figure 1. EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent Provides Superior RBC Depletion Compared to Ammonium Chloride Lysis
Different types of RBC-containing samples from normal healthy donors were processed to remove RBCs by using either ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) lysis or immunomagnetic depletion with EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent. After RBC removal, samples were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated anti-CD45 and anti-Glycophorin A antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. Residual RBCs were identified as Glycophorin A+/CD45− events. (A) The percentages of residual RBCs in various samples following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent was significantly lower compared to samples treated with ammonium chloride (mean ± SD; n = 31). (B) Both, RBC lysis with ammonium chloride and RBC removal using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent resulted in an equivalent total number of white blood cells recovered from whole blood samples (mean ± SD; n = 37).
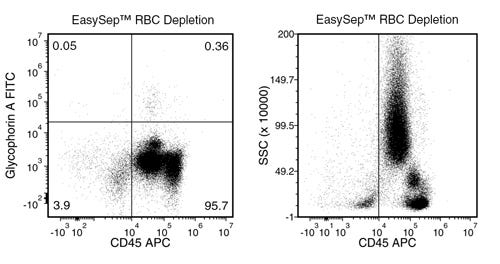
Figure 2. Typical RBC Removal Using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent With Human Whole Blood Samples
Starting with human whole blood from normal healthy donors, the percentage of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+/CD45-) following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent is typically 2 ± 3 (mean ± SD; n = 31). In the above example, the residual RBC content is 0.05%.
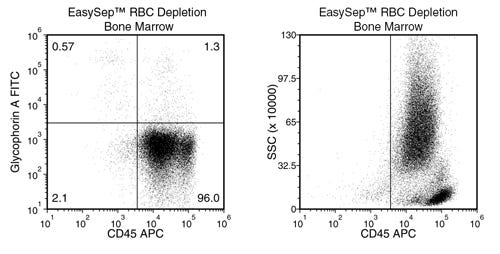
Figure 3. Typical RBC Removal Using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent With Human Bone Marrow Samples
Starting with human bone marrow, the percentage of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+/CD45-) following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent is typically 0.39 ± 0.34 (mean ± SD; n = 5). In the above example, the residual RBC content is 0.57%.
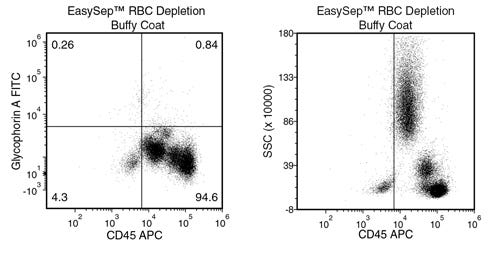
Figure 4. Typical RBC Removal Using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent With Buffy Coat Samples
Starting with buffy coat, the percentage of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+/CD45-) following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent is typically 0.12 ± 0.08 (mean ± SD; n = 6). In the above example, the residual RBC content is 0.26%.
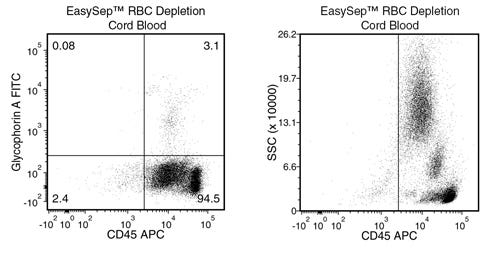
Figure 5. Typical RBC Removal Using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent With Cord Blood Samples
Starting with cord blood, the percentage of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+/CD45-) following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent is typically 1.7 ± 2.2 (mean ± SD; n = 16). In the above example, the residual RBC content is 0.08%.
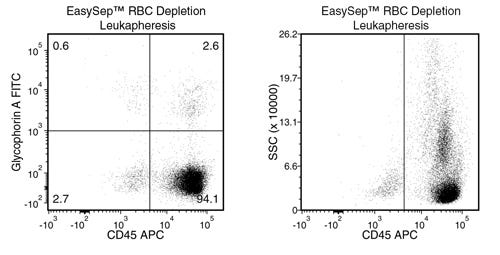
Figure 6. Typical RBC Removal Using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent With Leukapheresis Samples
Starting with leukapheresis samples, the percentage of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+/CD45-) following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent is typically 0.5 ± 0.8 (mean ± SD; n = 15). In the above example, the residual RBC content is 0.6%.
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (14)
Related Products
-
 Ammonium Chloride Solution
Ammonium Chloride SolutionReagent for lysis of red blood cells
-
 Lymphoprep™
Lymphoprep™Density gradient medium for the isolation of mononuclear cells
-
 HetaSep™
HetaSep™For depletion of red blood cells from fresh blood samples and isolation of nucleated cells
-
 EasySep™ Dead Cell Removal (Annexin V) Kit
EasySep™ Dead Cell Removal (Annexin V) KitImmunomagnetic depletion cell isolation kit
Item added to your cart

EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent
Quality Statement:
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.

Loading...













