High-Throughput Immunodensity-Based Cell Subset Isolation Directly from Whole Blood
- Document # 28726
- Version 2.1.0
- Dec 2024
Case Study: High-Throughput Isolation of Natural Killer Cells for the Assessment of In Vitro Cytotoxicity Using the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ System
In order to streamline the workflow of immune cell separation directly from whole blood samples and achieve high-throughput sample processing, Dr. Ajay Jain’s lab at the University of Maryland School of Medicine adopted a fast and efficient natural killer cell isolation method—the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system. This technical bulletin discusses how this rapid cell isolation system, which relies on immunodensity, reduced the time to obtain cells from 450 mL of blood from four hours to a single hour without compromising cell function or performance in downstream assays.
Background
The Need For High-Throughput Cell Isolation
Immune cell isolation plays an important role in areas such as drug discovery and development, vaccine research, and translational immunology. For example, isolating immune cells is routinely necessary to evaluate the efficacy of immunostimulatory compounds, assess the immunogenicity of vaccine candidates, or investigate interactions between the immune system and infectious agents.1-4
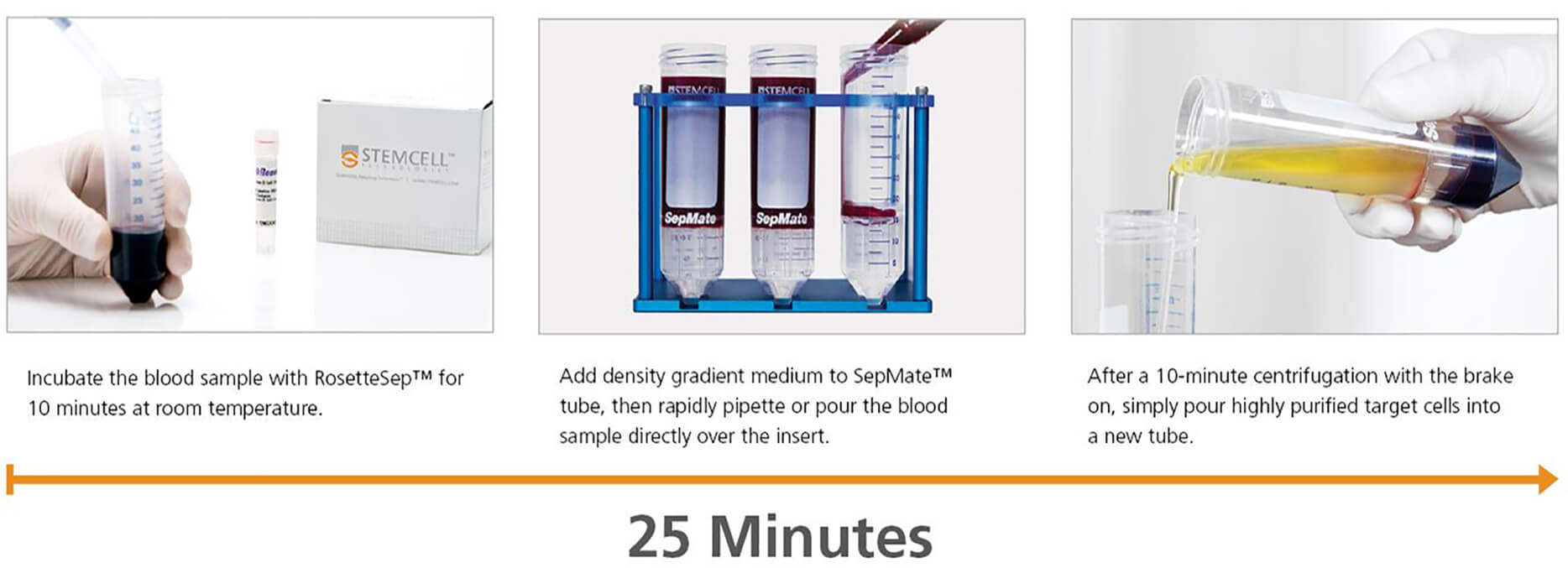
The movement towards more physiologically relevant assays based on primary human cells has created the need for a fast and efficient method of isolating immune cells from large numbers of whole blood samples.2,4 To facilitate this type of high-throughput cell processing, STEMCELL Technologies developed the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system that rapidly isolates cells directly from whole blood in as little as 25 minutes.
The RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system combines a unique immunodensity cell isolation reagent (RosetteSep™) with a specialized cell processing tube (SepMate™) to reduce the number of steps needed for cell isolation. This saves time, minimizes variability between users, and allows for efficient, high-throughput sample processing. Using this cell isolation system results in untouched and highly purified cells without the need for columns or immunomagnetic beads. Cells are immediately available for use in a variety of downstream assays, such as cytotoxicity testing, compound screening, and other applications where it is important to obtain viable, functional cells with minimal manipulation.
Evaluation of the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ System
Traditional methods for isolating lymphocytes from blood are laborious and time-consuming, and require technical expertise and precision. These methods typically involve isolating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by density gradient centrifugation (DGC) before enriching specific cell subpopulations using immunomagnetic column-based systems. At the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Dr. Ajay Jain and colleagues routinely isolate natural killer (NK) cells from large numbers of human samples. Isolating NK cells from a 450 mL unit of blood by DGC followed by immunomagnetic column-based selection can take up to 4 hours. In addition, following this method makes it difficult to process multiple samples quickly and efficiently.5 In order to find solutions to streamline their workflow and achieve higher- throughput sample processing, Jain’s lab evaluated the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system and assessed its impact on NK cell marker expression and cell cytotoxicity.
Methods
Dr. Jain’s group assessed and compared the in vitro cytotoxicity of NK cells that were isolated from 450mL of whole blood using two different methods: DGC followed by column-based immunomagnetic cell isolation or the RosetteSep™ Human NK Cell Enrichment Cocktail and SepMate™ cell isolation system (Catalog #15065 and Catalog #85450), as previously described.5 NK cellular cytotoxicity was then assessed against HT29 colon cancer and K562 leukemia target cells using a chromium release assay. Expression of NK cell activation markers was assessed using flow cytometry.
Results
Dr. Jain’s group found that isolation of NK cells was significantly faster with the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system: a 450 mL unit of blood could be split into multiple samples and processed in a single hour. Comparitavely, NK cell isolation by DGC followed by column-based immunomagnetic selection (DGC/immunomagnetic selection) took up to four hours.5
NK cells isolated by RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ were highly purified (86.7% as assessed by flow cytometry) with intact cytolytic function. To quantify the cytolytic activity of effector cells, Dr. Jain’s group used an in vitro assay to assess the capacity of NK cells to kill target HT29 colon cancer cells (Figure 1) and K562 leukemia cells (not shown here). HT29 cells express high levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and are susceptible to NK-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in the presence of anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab.6 The results showed that NK cells isolated with the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system retain the capacity to kill HT29 colon cancer cells by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (Figure 1) and K562 leukemia cells by direct cell-mediated killing (not shown here).5 Flow cytometric evaluation of NK cell activation markers demonstrated that NK cells isolated using RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ have similar expression profiles to cells isolated using DGC/immunomagnetic selection (Figure 2).5
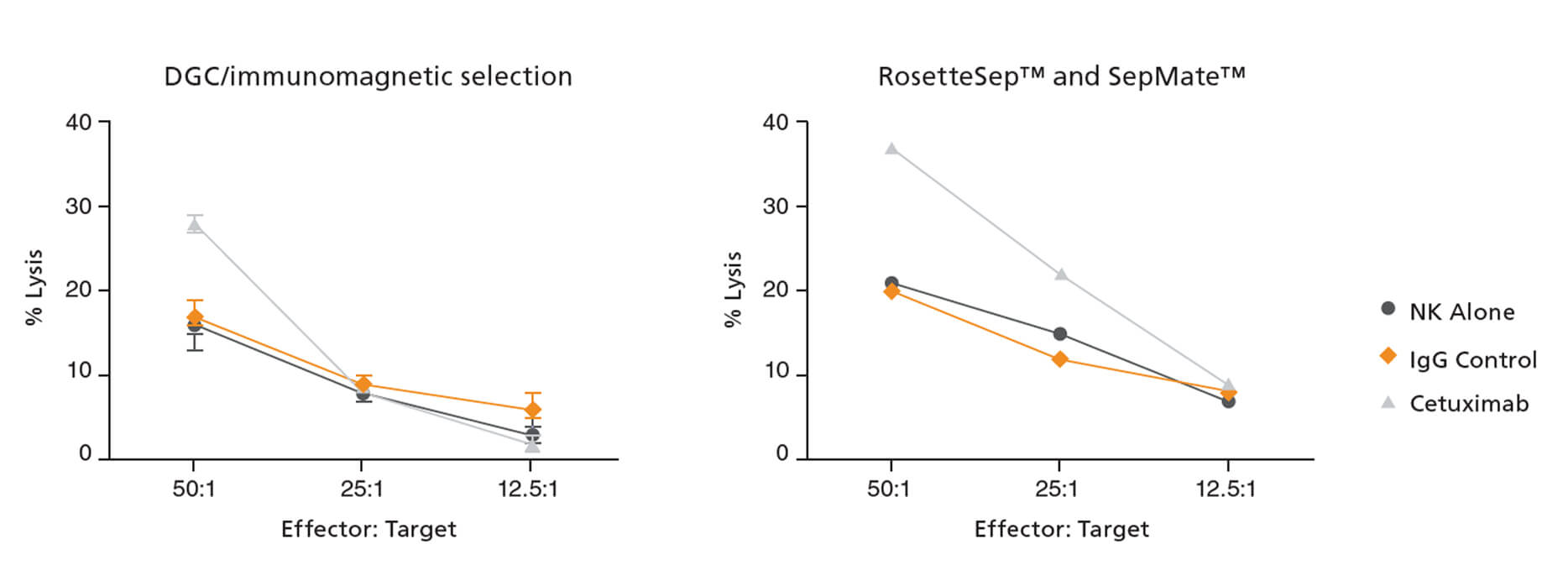
Figure 1. NK Cells Isolated with RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ Exhibit In Vitro Cytotoxicity.
NK cell in vitro cytotoxicity against HT29 colon cancer cells was assessed with cells isolated by DGC followed by immunomagnetic selection (left panel) or RosetteSep™ Human NK Cell Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15065) and SepMate™ (Catalog #85450) (right panel). In vitro conditions included culture with media alone (circles), 10 μg/mL human IgG1 isotype control (diamonds), or 10 μg/mL cetuximab (triangles). The figure shows the results of one representative experiment. Figure courtesy of Dr. Ajay Jain.
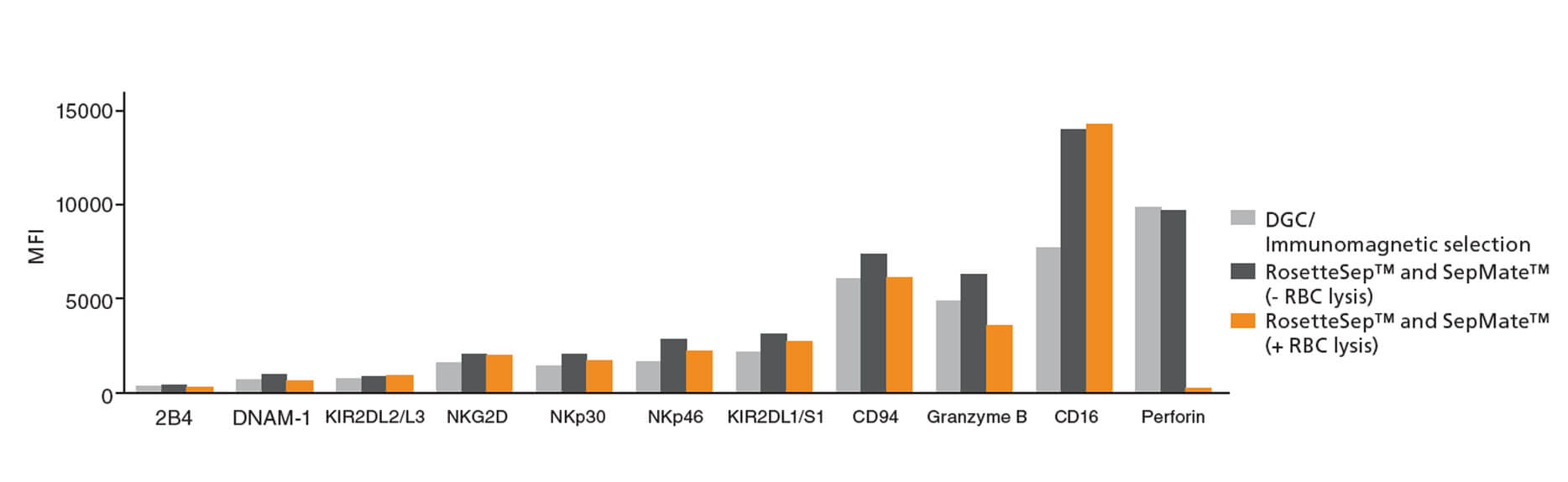
Figure 2. Surface expression of NK cell activation markers as evaluated by flow cytometry.
NK cells were isolated by DGC followed by immunomagnetic selection (DGC/Immunomagnetic selection), RosetteSep™ Human NK Cell Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15065) and SepMate™ (Catalog #85450), or RosetteSep™ Human NK Cell Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15065) and SepMate™ (Catalog #85450) followed by red blood cell (RBC) lysis. The surface and intracellular expression of NK cell activation markers was evaluated by flow cytometry. Expression is shown as mean fluorescent intensity (MFI). The expression of surface and intracellular activation markers, aside from CD16, is comparable between NK cells isolated by DGC/immunomagnetic selection and NK cells isolated with RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ in the absence of RBC lysis. Figure courtesy of Dr. Ajay Jain.
"The SepMate™ tubes… provide a mechanical barrier between the purified effector cells and the density gradient medium. The desired cell populations remain above the barrier and can be poured out of the tube with no technical expertise. This method allows for the concurrent rapid purification of NK cells and CD8+ and CD4+ T cells from multiple human donors, which makes downstream applications (i.e. flow cytometry, ELISA, assessment of in vitro cytotoxicity) more practical to perform in a high-throughput manner."
So EC et al. (2013)
Conclusions
The RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system allows efficient negative isolation of cell subsets directly from whole blood in a quarter of the time compared to density gradient centrifugation followed by column-based immunomagnetic selection. The RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system requires no technical expertise, facilitates rapid cell isolation from many samples at once, and yields fully functional cells for highthroughput downstream assays. For more information on the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ system and how it works, see page 3.
How the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ System Works
RosetteSep™
RosetteSep™ isolates highly purified cells directly from blood by crosslinking unwanted cells to red blood cells, forming immunorosettes. These immunorosettes pellet during density gradient centrifugation, leaving untouched and highly purified target cells at the interface between the plasma and the density gradient medium.
The SepMate™ Advantage
Using the SepMate™ tube makes the RosetteSep™ procedure even faster and easier. The SepMate™ insert creates a physical barrier between the sample and density gradient medium, allowing the sample to be rapidly pipetted or poured into the tube. Centrifugation time is reduced to just 10 minutes, and purified target cells can simply be poured into a new tube. SepMate™ can also be used on its own for hassle-free PBMC isolation from whole blood in just 15 minutes.
Why Use the RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ System?
- Isolate untouched cell subsets from whole blood during your standard density gradient centrifugation step in as little as 25 minutes.
- Choose from a wide range of RosetteSep™ reagents to isolate the cell subset of your interest.
- Obtain highly purified, unlabeled, viable, and functional cells.
- Eliminate errors with an easy-to-use system that does not require columns, magnets, or other special equipment.
- Combine RosetteSep™ with SepMate™ to minimize variability between separation, or use RosetteSep™ on its own.
The RosetteSep™ and SepMate™ Procedure
Watch a video showing how to combine SepMate™ with RosetteSep™ for fast cell subset isolation directly from whole blood.
Product Listing
Select RosetteSep™ Products for Cell Isolation by Negative Selection
Select RosetteSep™ Products Cell Depletion Cocktails
SepMate™ Products
1. SepMate™ (IVD) is available in Australia, Canada, Europe, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America, as an In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) device for the isolation of mononuclear cells from human whole blood and bone marrow by density gradient centrifugation. This product is also available in China where it is considered a non-medical device by the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA), and should therefore be used as general laboratory equipment.
2. SepMate™ for Research Use Only (RUO) is available in regions where SepMate™ is not
registered as an IVD device.
Fresh Human Peripheral Blood Products
CP2D2
EDTA2
Na Heparin2
1. Fresh products (excluding bone marrow), currently available in the United States and Canada
(excluding Quebec). Fresh bone marrow currently available in the United States only. Please
contact Product and Scientific Support (techsupport@stemcell.com) for further information.
2. ACDA - Acid Citrate Dextrose Solution A; CP2D - Citrate-Phosphate-Double Dextrose; EDTA -
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid; Na Heparin - Sodium Heparin
Density Media
1. Lymphoprep™ has the same density as Ficoll-Paque® and can be substituted for Ficoll-Paque® without any need to change your existing protocols.
References
- World Health Organization. (2005) WHO Guidelines on Nonclinical Evaluation of Vaccines. Technical Report Series, No. 927. Clin Transplant 18(5): 558–563.
- Slater K. (2001) Cytotoxicity tests for high-throughput drug discover. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12(1): 70–4.
- McMillin DW et al. (2012) Compartment-Specific Bioluminescence Imaging platform for the High-throughput evaluation of antitumor immune function. Blood 119(15): e131–8.
- Sáez-Cirión A et al. (2010)Ex vivo T cell-based HIV suppression assay to evaluate HIV-specific CD8+ T-cell responses. Nat Protoc 5(6):1033–41.
- So EC et al. (2013) A high throughput method for enrichment of natural killer cells and lymphocytes and assessment of in vitro cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 394(1–2): 40–8.
- Schlaeth M et al. (2010) Fc-engineered EGF-R antibodies mediate improved antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against KRAS-mutated tumor cells. Cancer Sci 101(5): 1080–8.
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration