How to Characterize Extracellular Vesicles by Western Blotting
How to characterize extracellular vesicles and analyze for presence of characteristic EV protein markers by western blotting
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid bilayer-enclosed structures released by almost all cell types. These vesicles, carrying protein and genetic cargo, play an important role in intercellular communication and are recognized for their potential therapeutic applications. Due to their inherently heterogeneous nature as well as the complexity of biological samples, it is recommended to characterize EVs after isolation.
There are several ways for isolating EVs from biofluids or cell culture conditioned media (e.g. MesenCult™-ACF Plus Medium), such as immunomagnetic separation, differential ultracentrifugation, or size exclusion chromatography (SEC)*. Using EasySep™ Human Extracellular Vesicle Positive Selection Kits or Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns, researchers can easily isolate and purify human EVs from biofluids—including serum and plasma—and from culture-conditioned media. Once isolated, the particles should be analyzed to confirm that they are indeed EVs and not products of cell fragmentation or other contaminants such as protein complexes or lipoproteins, usually present in biological samples.
Isolated EVs can be characterized by western blotting (also referred to as immunoblotting), a widely used technique to detect specific protein markers in a sample. Tetraspanin markers such as CD9, CD63, and CD81 are proteins commonly found on EVs across different cell types. Here, we provide a detailed protocol for performing a western blot to detect the presence of such characteristic EV-associated proteins in order to confirm the presence of EVs in the biological sample.
* For information regarding isolation of EVs using EasySep™, refer to the Product Information Sheets (PIS) for EasySep™ Human Pan-Extracellular Vesicle Positive Selection Kit, EasySep™ Human Extracellular Vesicle (CD81) Positive Selection Kit, EasySep™ Human Extracellular Vesicle (CD9) Positive Selection Kit, EasySep™ Human Extracellular Vesicle (CD63) Positive Selection Kit or EasySep™ Extracellular Vesicle PE Positive Selection Kit.For information regarding isolation of EVs using SEC Columns, refer to the associated PIS for Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns.
Materials
- 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer (Bio-Rad Catalog #1610747)
- Tris-hydrochloride (Tris-HCl)
- Glycine
- Distilled water (dH2O)
- 10% Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in dH2O
- Methanol (MeOH)
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA)
- TWEEN® 20
Protocol
I. Buffer Preparation
- Prepare Transfer Buffer by combining the components in the order listed in Table 1. Mix thoroughly.
Table 1. Preparation of Transfer Buffer
ComponentFinal ConcentrationAmount to Prepare 1LTris-HCl48 mM5.8 gGlycine39 mM2.9 g10% SDS0.0375%3.75 mLdH2O-800 mLMeOH20%200 mL - Prepare Blocking Buffer by adding the components listed in Table 2. Mix the solution thoroughly after adding each component. Or use a chemical blocking buffer (e.g. EveryBlot Blocking Buffer Bio-rad Cat# 12010020).
Table 2. Preparation of Blocking Buffer
ComponentsFinal ConcentrationAmount to Prepare 10 mLBSA5%0.5 gTWEEN® 200.2%20 µLPBS-10 mL - Prepare Wash Buffer by adding 1 mL of TWEEN® 20 in 1 L PBS.
- Isolate EVs using EasySep™ Human Extracellular Vesicle Positive Selection Kits or Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns.
- Fully resuspend EVs in residual liquid from the isolation process and adjust to the desired volume. For instance, EVs isolated from 1 mL of plasma can be adjusted to a final volume of 250 µL. Store isolated EVs in a low-binding tube to reduce EV loss to the sample tube. Set aside 30 µL for western blot analysis.
- Dilute 3 parts sample with 1 part 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer.
Note: When blotting for CD9, CD63, CD81, EpCAM, and CD45, do not add a reducing agent to the Laemmli Sample Buffer, as CD9/CD63/CD81 detection antibodies often recognize the disulfide bond on the antigen's epitope.- EV markers other than CD9/CD63/CD81/CD45/EpCAM may require a reducing agent added to Laemmli Sample Buffer. When uncertain, test 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer with and without reducing reagent. To prepare 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer with reducing agent, add 100 µL of 2-mercaptoethanol to 900 µL of 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer, or add dithiothreitol to 4X Laemmli Sample Buffer to a final concentration of 50 mM.
- If you used EasySep™ to isolate the EVs, the antibodies from EasySep™ Positive Selection Cocktail may be detected by secondary antibodies. In this case, it is recommended to run a small volume of the Positive Selection Cocktail to check for background signals.
- Heat the samples at 95°C for 5 minutes.
- Load the desired volume (e.g. 35 µL) of samples per well in a 10% polyacrylamide gel.
- Run SDS-PAGE for 30 minutes at 200 V.
- Rinse gel twice with distilled water. Incubate gel in cold Transfer Buffer for 15 minutes.
- Assemble transfer sandwich as per instrument instruction and then transfer the proteins onto a PVDF membrane.
- If using semi-dry transfer, use 10 V for 30 minutes.
- If using wet transfer, use 100 V for 60 minutes.
Note: Use a low-fluorescence PVDF membrane or nitrocellulose membrane for fluorescence imaging. - Rinse the membrane twice with PBS and incubate with Blocking Buffer at room temperature for 1 hour with rocking (If chemical blocking buffer is used, follow manufacturer recommendation for blocking time. E.g 5 minutes for EveryBlot Blocking Buffer).
- Wash the membrane 2X for 5 minutes each with Wash Buffer.
Recommended western blot primary and secondary antibody antibodies combinations:Primary Antibody (Catalog #) Conjugation Final Primary Antibody Concentration (µg/mL) Secondary Antibody/Detection Agent Clone Secondary Antibody Dilution Final Concentration (µg/mL) Anti-Human CD9, Clone HI9a (100-0138) Unconjugated 0.5 - 1.0 Goat anti-mouse HRP Polyclonal 1:5000 0.08 Anti-Human CD63, Clone H5C6 (100-0139) Unconjugated 1.0 - 2.0 Anti-Human CD81, Clone 5A6 (100-0209) Unconjugated 0.5 - 1.0 Anti-Human EpCAM, Clone 9C4 Biotin (preferred),
Unconjugated0.5 - 1.0 Anti-Human CD45, Clone HI30 (60018BT) Biotin 0.5 - 1.0 Streptavidin HRP - 1:5000 0.1 Anti-Mouse CD63, Clone, NVG-2 Biotin 0.5 - 1.0 - Dilute primary antibodies in the blocking buffer.
- Incubate the membrane with primary antibodies at room temperature for 1 hour.
- Wash membrane 3X for 5 minutes each with Wash Buffer. Incubate membrane with secondary antibodies at room temperature for 1 hour.
- Wash the membrane 3X for 5 minutes each with Wash Buffer.
- To detect signals, incubate blot with chemiluminescence substrate and image. To detect a signal from fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies, use fluorescence imaging.
Recommended substrate for western blot detection:Antigen Recommended Substrate Sensitivity Human CD9 Mid-femtogram (e.g. Bio-rad Clarity Western ECL substrate Cat#1705061) Human CD63 Human CD81 Human EpCAM Low picogram to femtogram (e.g. Sigma Chemiluminescent Peroxidase Substrate Cat# CPSOC-100ML) Human CD45 Mouse CD63 Low femtogram to high-attogram (e.g. SuperSignal™ West Atto Ultimate Sensitivity Substrate Cat# A38555)
II. EV Sample Preparation
III. SDS-PAGE
IV. Immunoblotting and Imaging
Data
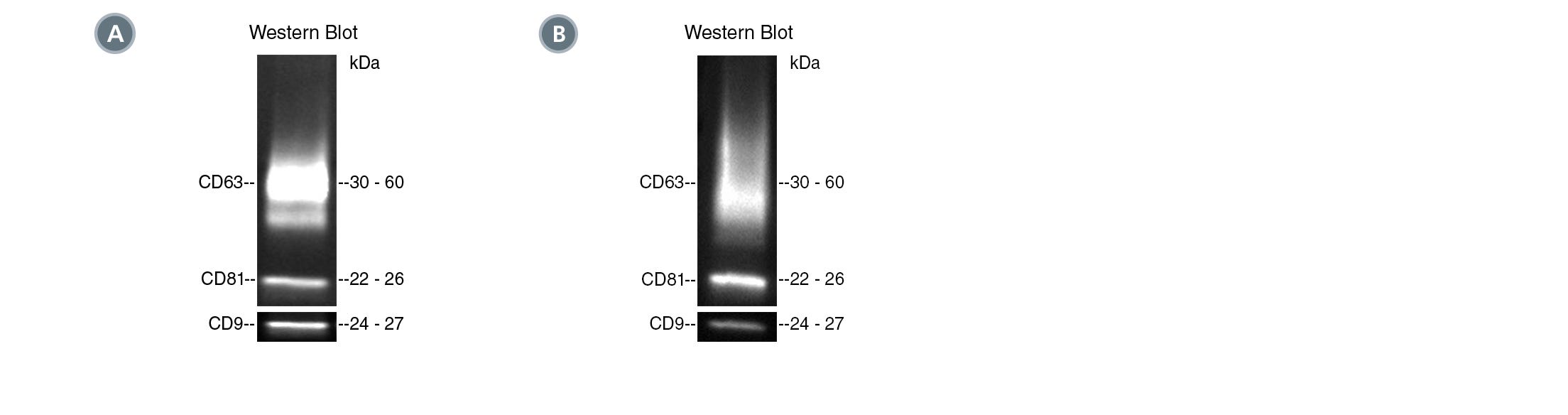
Figure 1. Typical Western Blot Analyses of EVs Isolated from Human Plasma and Mouse Plasma
(A) EVs were isolated from healthy human plasma spiked with cancer cell (MCF7)-derived EVs by differential ultracentrifugation (UC) or using the following PE-conjugated antibodies with EasySep™ Extracellular Vesicle PE Positive Selection Kit: Anti-Human CD45 Antibody, Clone HI30 (Catalog #60018PE); Anti-Human EpCAM Antibody, Clone 9C4; and Mouse IgG1, kappa Isotype Control Antibody, Clone MOPC-21 (Catalog # 60070PE). Target markers (EpCAM and CD45) and common EV markers (CD9, CD81, and CD63) were analyzed by western blot under non-reducing conditions.
(B) EVs were isolated from mouse plasma using PE-conjugated Anti-Mouse CD63 Antibody, Clone NVG-2 or PE-conjugated Rat IgG2a Isotype Control Antibody with the EasySep™ Extracellular Vesicle PE Positive Selection Kit. Target marker (CD63) was analyzed by western blot under non-reducing conditions.
Related Materials
Highly pure human EVs can be easily obtained in as little as 30 minutes with EasySep™ immunomagnetic separation. Explore all our products for EV isolation and characterization below.
Products for Isolation of EVs Using Immunomagnetic Separation
Products for Isolation of EVs Using Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Products for Characterization of EVs
Reference
- Kowel EJK et al.(2017) Extracellular vesicle isolation and analysis by western blotting. Methods Mol Biol. 1660:143–52.
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration




