EpiCult™ Media for Mammary Epithelial Cell Culture
EpiCult™ Mammary Cell Culture Media
Serum-Free, Defined Media for Mammary Epithelial Cell Culture
EpiCult™-C: Culture Human Mammary Epithelial Cells
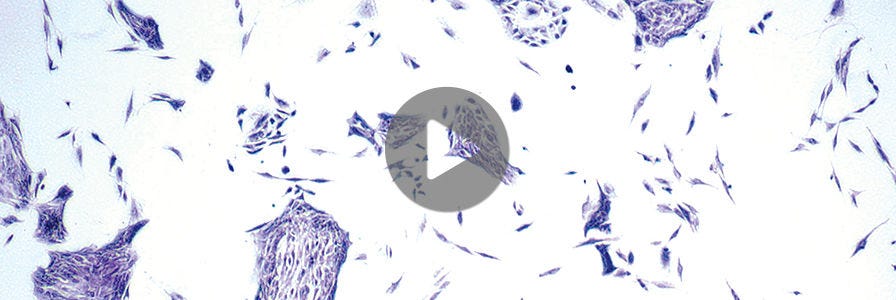
EpiCult™-C Medium is optimized to support the short term culture of human mammary luminal epithelial and myoepithelial cells. It can also be used for the enzymatic dissociation of human mammary tissue when supplemented with Collagenase/Hyaluronidase. Watch this video to learn more.
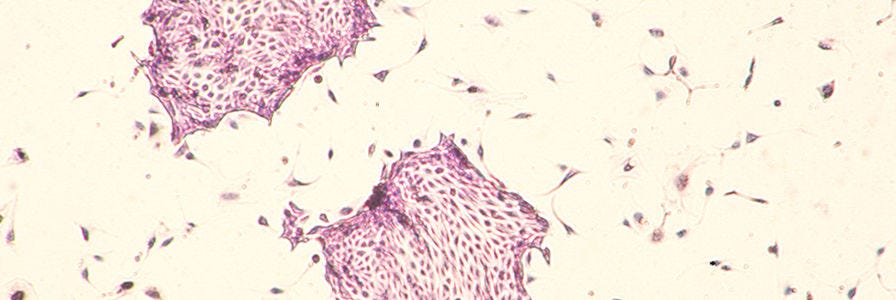
EpiCult™-B: Detect Human or Mouse Mammary Colony-Forming Units (Ma-CFUs)
EpiCult™-B has species-specific formulations for the culture and assay of either human or mouse mammary cells. Detect the presence of mammary precursor cells in Ma-CFUs for quantification, or in 3D Matrigel®-based cultures for an environment that is representative of the in vivo mammary duct structure.
Key Applications
Publications on Normal Mammary Cells
EpiCult™-B (Human)
Raouf A et al. (2008) Transcriptome analysis of the normal human mammary cell commitment and differentiation process. Cell Stem Cell 3(1): 109-18.
Stingl J et al. (2001) Characterization of bipotent mammary epithelial progenitor cells in normal adult human breast tissue.Breast Cancer Res Treat 67(2): 93-109.
EpiCult™-B (Mouse)
Stingl J et al. (2001) Characterization of bipotent mammary epithelial progenitor cells in normal adult human breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 67(2): 93-109.
Publications on Cancerous Cells
EpiCult™-B (Human)
D'Uva G et al. (2013) Beta-Catenin/HuR Post-Transcriptional Machinery Governs Cancer Stem Cell Features in Response to Hypoxia. PLoS one 8(11) e80742.
Law JH et al. (2010) Molecular decoy to the Y-box binding protein-1 suppresses the growth of breast and prostate cancer cells whilst sparing normal cell viability. PLoS One 5(9): e12661.
Diehn M et al. (2009) Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature 458(7239): 780-3.
Lindvall C et al. (2006) The Wnt signaling receptor Lrp5 is required for mammary ductal stem cell activity and Wnt1-induced tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 281(46): 35081-7.
EpiCult™-B (Mouse)
Teissedre B et al. (2009) MMTV-Wnt1 and -DeltaN89beta-catenin induce canonical signaling in distinct progenitors and differentially activate Hedgehog signaling within mammary tumors. PLoS ONE 4(2): e4537.
Shimono Y et al. (2009) Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 138(3): 592-603.
Shafee N et al. (2008) Cancer stem cells contribute to cisplatin resistance in Brca1/p53-mediated mouse mammary tumors. Cancer Res 68(9): 3243-50.