Immune Tolerance
Immune tolerance is critical to prevent the development of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Although the concept of tolerance has long been established, researchers continue to uncover previously unknown mechanisms and therapeutic applications of immune tolerance.
Below is a collection of scientific resources for your immune tolerance research.
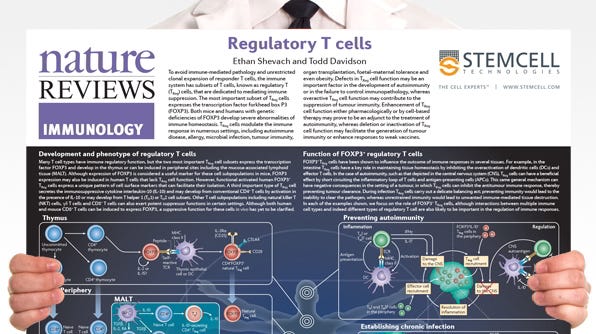
Regulatory T Cells
Ethan Shevach and Todd Davidson. This poster provides an updated overview of the development, phenotype and functions of regulatory T cells, in particular those subsets that express the transcription factor forkhead box P3 (FOXP3).
Get Your Free Copy >Immune tolerance is critical to prevent the development of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. There are several mechanisms of tolerance, which can be broadly categorized as either central or peripheral tolerance. Central tolerance prevents the maturation and egress of autoreactive immune cells, for example via clonal deletion of T cells in the thymus. Any autoreactive cells that escape central tolerance and migrate to the periphery would then encounter mechanisms of peripheral tolerance, for example the induction of anergy or suppression by mechanisms of action of regulatory T cells. Although the concept of central and peripheral tolerance has long been established, researchers continue to uncover previously unknown mechanisms of immune tolerance.
Immune Tolerance
In 2003, the role of FOXP3 in regulatory T cells (Tregs) was described’. Since then, the number of studies focusing on the immunosuppressive nature of Tregs has significantly grown. FOXP3 remains the most reliable marker of Tregs to date, and the importance of Tregs in maintaining immune tolerance continues to be highlighted.