PancreaCult™ Organoid Media (Human)
Culture media kits for initiation, growth, and establishment of human pancreatic organoids

Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
-
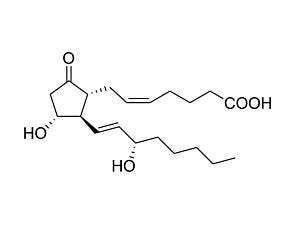 Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2Prostanoid pathway activator; Activates prostaglandin receptors EP1, EP2, EP3 and EP4
-
 Y-27632 (Dihydrochloride)
Y-27632 (Dihydrochloride)RHO/ROCK pathway inhibitor; Inhibits ROCK1 and ROCK2
-
 Human Recombinant EGF
Human Recombinant EGFEpidermal growth factor
-
Labeling Antibodies
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
Overview
Pancreatic organoids can be established from fresh or frozen dissociated tissue in PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM), optimized to provide higher rates of organoid formation from tissue. Organoids can then be cultured in PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (OGM) for long-term maintenance, passaging, serum-free drug screening, or cryopreservation for future experiments. The optional removal of EGF from the medium supports the depletion of normal cells in KRAS-activated cancer organoid cultures.
Organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ (Human) medium system can be adapted to various culture protocols, including two-dimensional Transwell® monolayer cultures, dilute Corning® Matrigel® suspension cultures, and high-throughput assay-compatible culture formats. Learn how to set up human pancreatic organoids for drug testing in high-throughput formats using the latest protocol .
Should you intend to use this product for commercial purposes, please contact HUB at www.huborganoids.nl for a commercial use license or for clarifications in relation to HUB licensing.
Data Figures
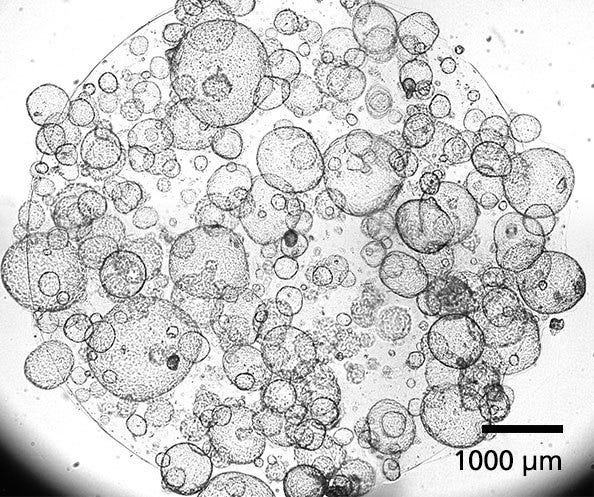
Figure 1. Human Pancreatic Duct Organoids
PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM; Human) and Organoid Growth Medium (OGM; Human) support the initiation and expansion of human pancreatic duct organoids from pancreatic tissue or previously established organoid cultures. Shown are organoids grown using PancreaCult™ OIM and OGM and imaged on day 7 of passage 3.
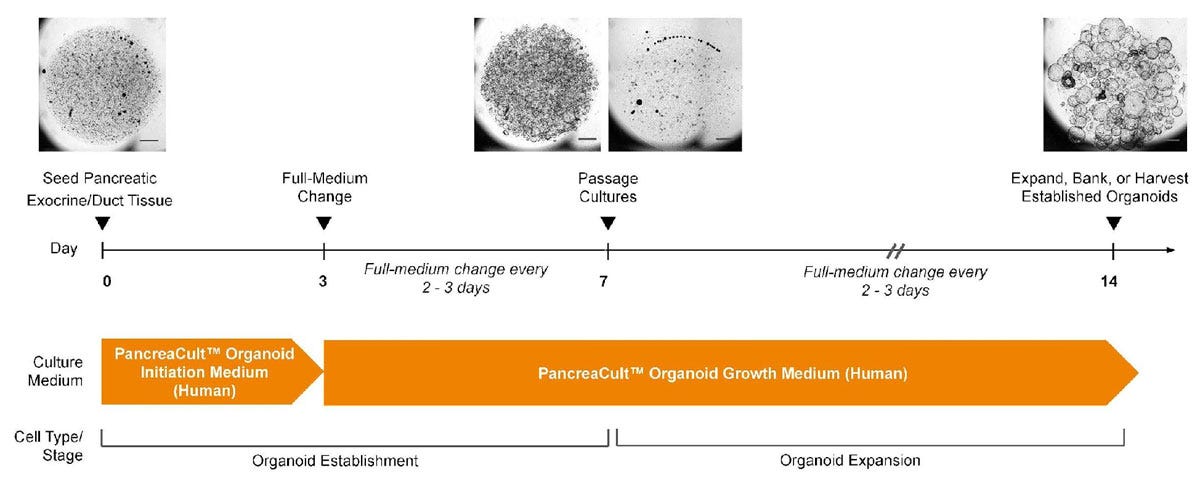
Figure 2. PancreaCult™ Human Enables Initiation and Expansion of Pancreatic Ductal Organoids
Human pancreatic ductal organoids are initiated in PancreaCult™ OIM for the first 3 days of culture, then switched to PancreaCult™ OGM for the remainder of culture. Alternatively, organoids can be grown in PancreaCult™ OGM for a completely serum-free protocol, however, proliferative pancreatic ductal cells are better supported in PancreaCult™ OIM during the first 3 days of culture. Cultures should be passaged after 7 days with further medium changes every 2-3 days. Pancreatic ductal organoids are suitable for experimentation or banking after one full passage in PancreaCult™ OGM. For full culture instructions please refer to the product manual (Document #10000011617)
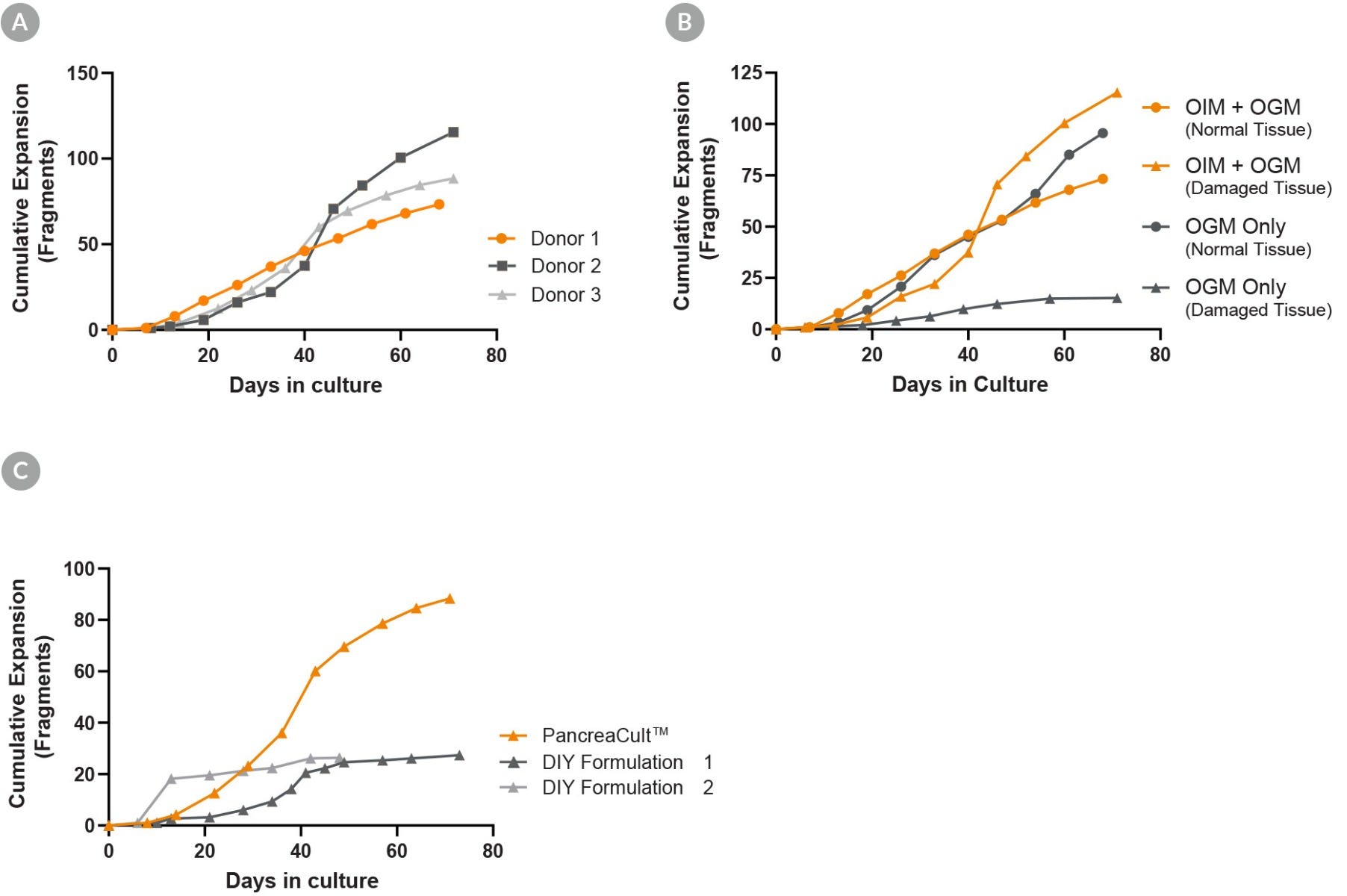
Figure 3. PancreaCult™ (Human) Provides Robust Expansion of Pancreatic Duct Organoids
(A) Organoid expansion in PancreaCult™ OGM provides robust expansion of organoids across different donors. (B) Organoids may be initiated in PancreaCult™ OGM for a completely serum-free workflow, however, initiation and maintenance of damaged tissue is better supported by initiating cultures in PancreaCult™ OIM. (C) Comparison of PancreaCult™ Human to two different DIY formulations showed more robust expansion of organoids in PancreaCult™ Human. Shown is the cumulative fold expansion of organoid fragments as counted at the end of each passage.
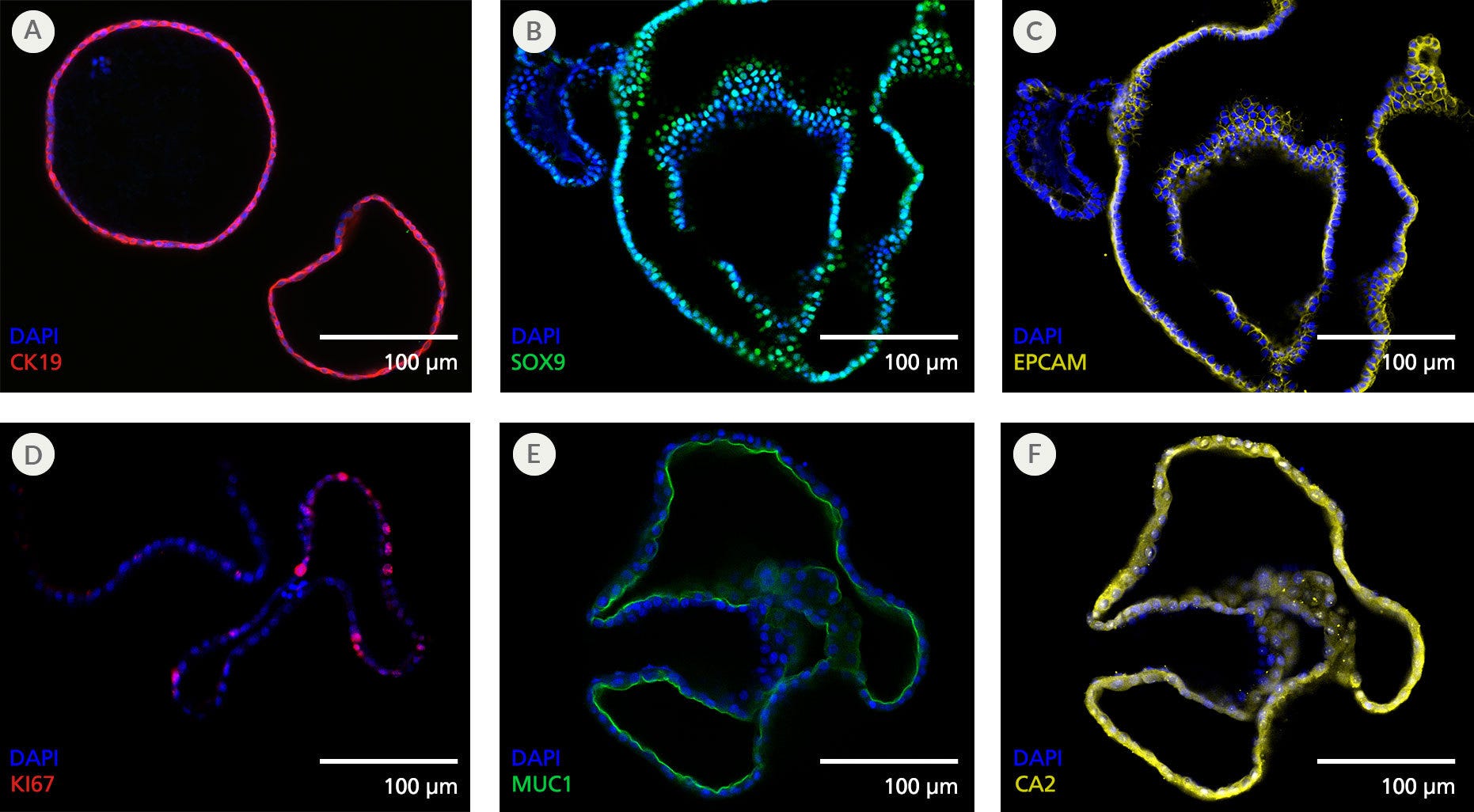
Figure 4. Pancreatic Duct Organoids Display Features of the Pancreatic Ductal Epithelium
Organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ (Human) display marker expression consistent with the pancreatic ductal epithelium when imaged using immunocytochemistry. Shown are organoids grown in PancreaCult™ OGM and stained for (A) pancreatic ductal marker CK19, (B) pancreatic ductal marker SOX9, (C) epithelial marker EPCAM, (D) proliferation marker KI67, (E) apical pancreatic duct marker MUC1, and (F) pancreatic ductal marker CA2. Organoids were imaged on passage 2 (A), passage 3 (B, C) or passage 10 (D-F).
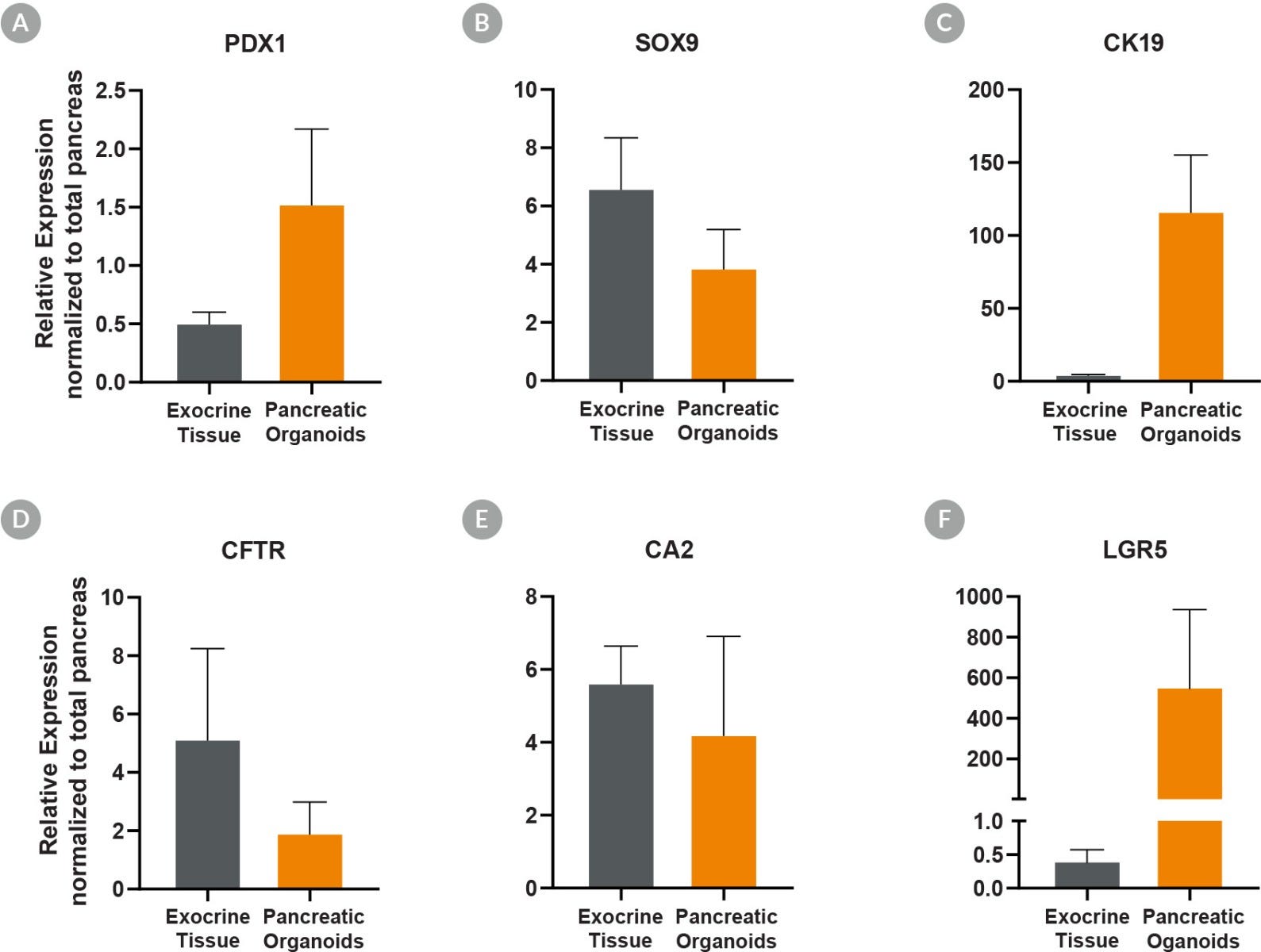
Figure 5. Pancreatic Duct Organoids Cultured With PancreaCult™ Human Show Pancreatic Marker Expression Levels Similar to Exocrine Tissue
Pancreatic duct organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ Human show marker expression levels similar to those observed in exocrine tissue. Analysis by qPCR showed pancreatic duct organoids were enriched for (A) PDX1 (C) CK19 and (F) LGR5 as compared to total pancreatic tissue, demonstrating enrichment of proliferative duct organoids. Comparable expression of (B) SOX9, (D) cystic fibrosis transmembrane receptor (CFTR), and (E) CA2 was observed in pancreatic duct organoids. Expression levels are normalized to TBP and UBC housekeeping genes (ΔCT) and total pancreas for relative expression levels (ΔΔCT).
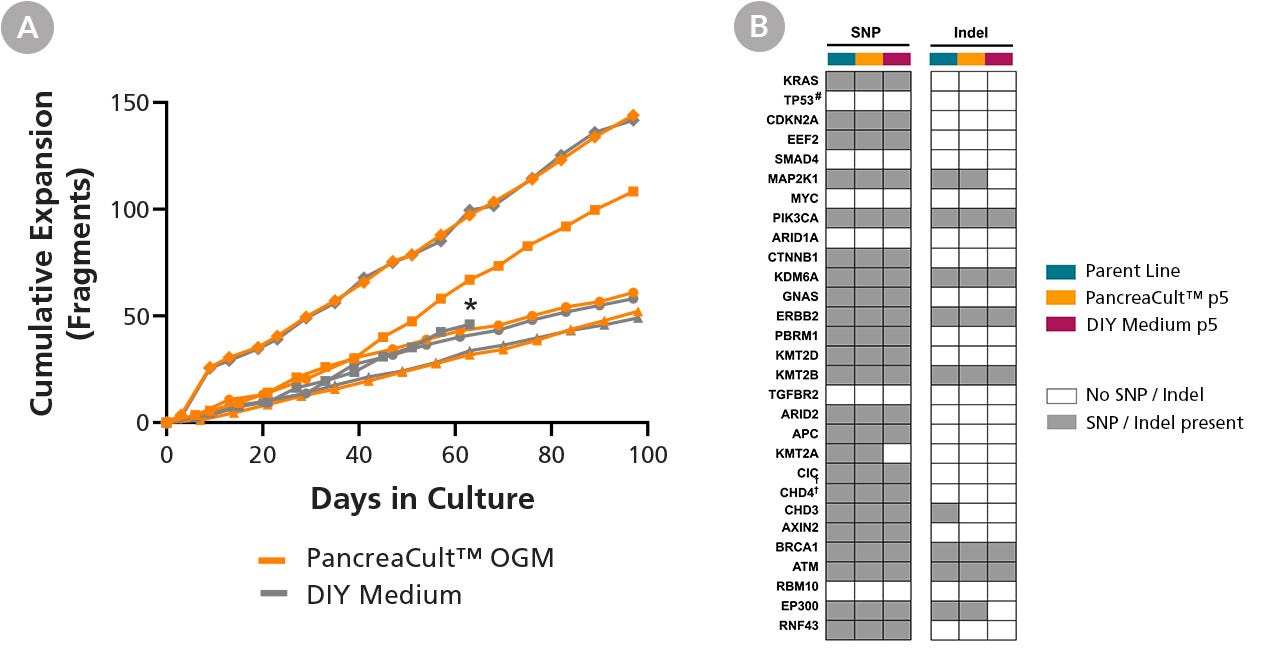
Figure 6. PancreaCult™ (Human) Efficiently Maintains the Long-Term Growth and Genetic Profile of PDAC (Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma) Organoids
(A) Pre-established PDAC organoid lines can be maintained and expanded in PancreaCult™ OGM for at least 10 passages (n = 4) and demonstrate comparable growth with PDAC organoid lines maintained in DIY media. *DIY medium culture for this line was terminated after 10 passages. (B) Pre-established PDAC organoids cultured in PancreaCult™ OGM for 5 passages retain somatic SNPs and indels in oncogenic driver and tumor suppressor genes from the parent PDAC organoid line. Whole-exome sequencing data was collected before (teal) and after 5 passages of PDAC organoid cultures in PancreaCult™ OGM (orange) or the DIY media (maroon). Grey and white boxes indicate the overall presence or absence of SNPs or indels in the indicated genes compared to the parent PDAC organoid line pre-established in DIY media. #TP53 reads were undetectable, indicating gene deletion.
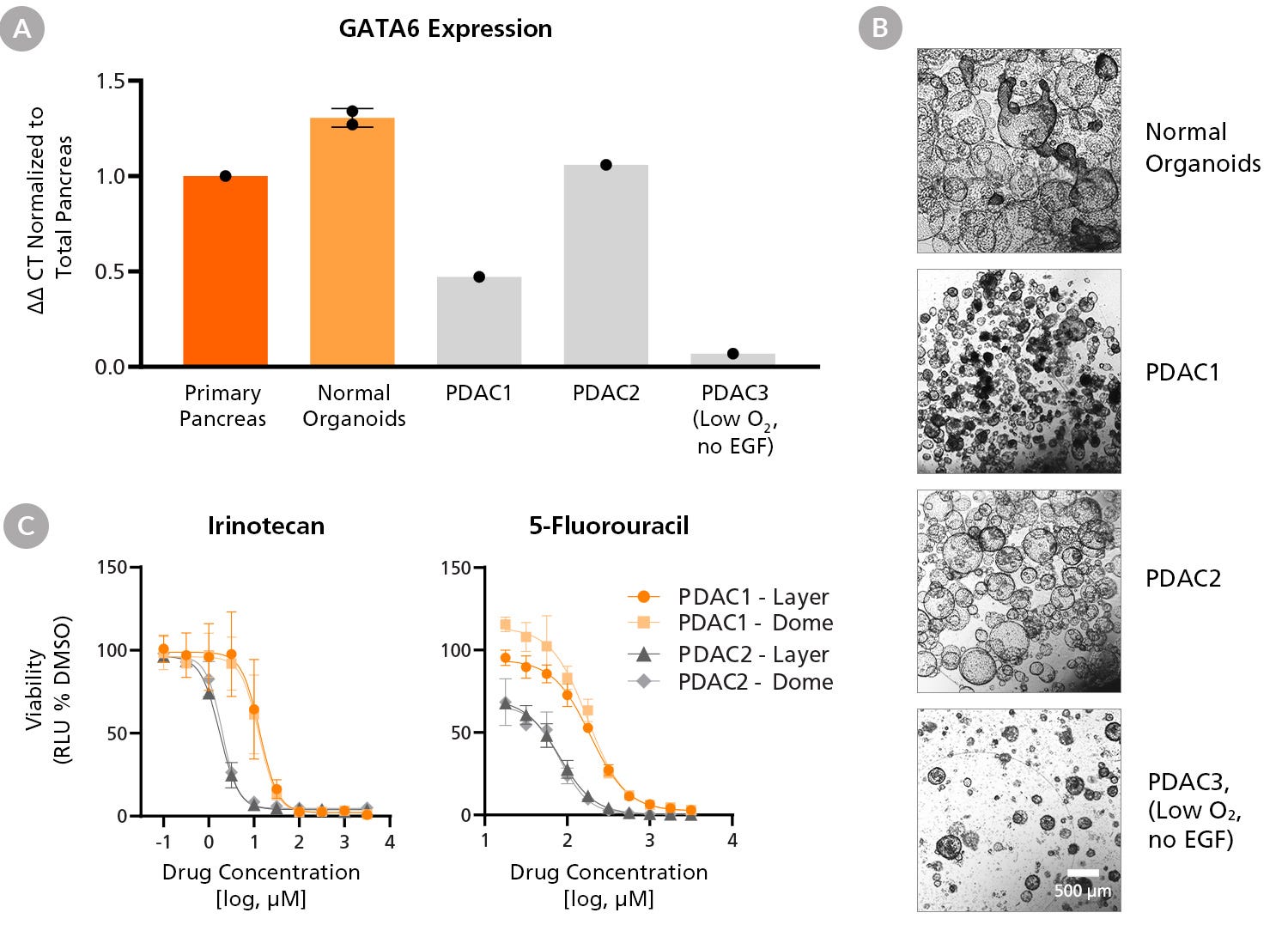
Figure 7. PDAC Organoid Line-Specific Differences in GATA6 Expression, Morphology, and Chemotherapy Drug Response
PDAC organoid lines (PDAC1-3) grown using PancreaCult™ (Human) demonstrate line-specific differences in (A) GATA6 (GATA-binding factor 6) gene expression and (B) morphology. Expression levels are normalized to housekeeping genes (ΔCT) and primary pancreatic tissue for relative expression levels (ΔΔCT). PDAC1 and PDAC2 lines were expanded in PancreaCult™ OGM from pre-established lines while normal organoids and the PDAC3 line were established with PancreaCult™ OIM from dissociated primary tissue and maintained in PancreaCult™ OGM. PDAC3 expansion was facilitated by reduced oxygen culture (5%) and maintained in the absence of EGF. Scale bar = 500 μm. (C) PDAC organoid lines were cultured in 96-well plates within Matrigel® domes or layer cultures and treated with irinotecan (left) or 5-fluorouracil (right) and compared to 0.1% DMSO vehicle control. Full-medium changes with fresh compounds were performed each day and analyses were performed 24 hours after the final fresh compound addition (Day 3). Cell viability for treated, vehicle-treated, and untreated PDAC organoid lines was assessed using the CellTiter-Glo® 3D Cell Viability Assay (Promega Catalog #G9681). Irrespective of layer or dome culture format, PDAC organoid lines demonstrate line-specific differences in chemotherapy drug response. Error bars = SD.
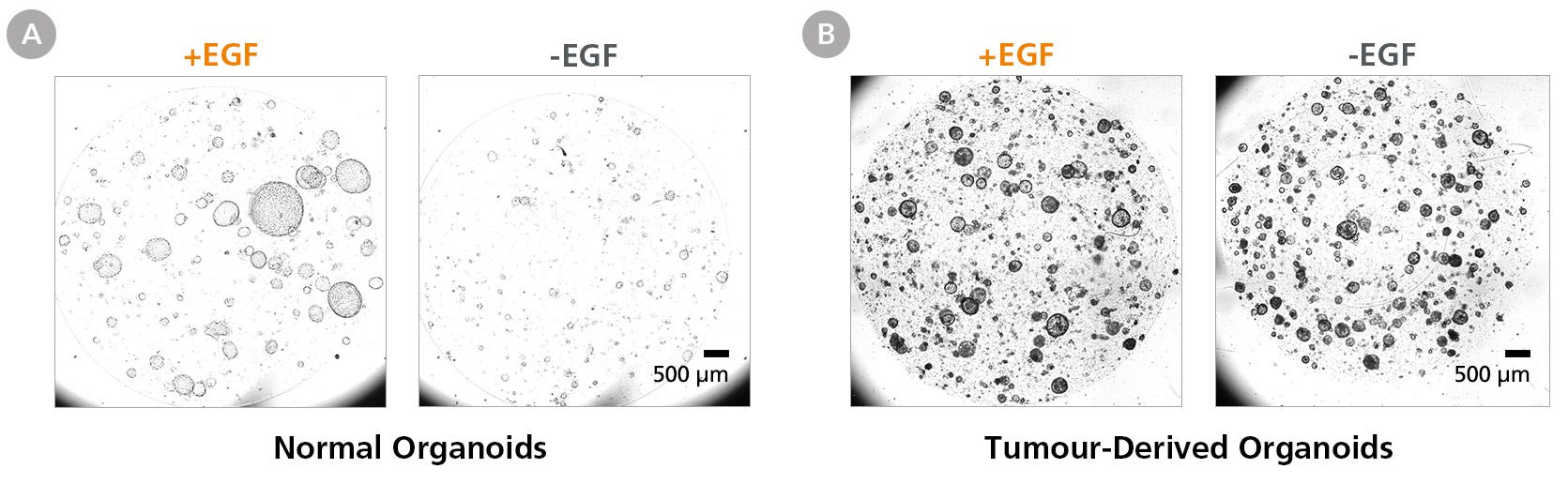
Figure 8. Removing Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Abrogates Normal Pancreatic Duct Organoid Growth but Does Not Affect PDAC Organoids Cultured in PancreaCult™ (Human)
(A) EGF removal efficiently suppresses normal pancreatic duct organoid growth within the first passage. (B) PDAC organoids were established in PancreaCult™ OIM and maintained in PancreaCult™ OGM for 8 passages in low-oxygen culture (5%) before removing EGF. EGF-depleted PDAC organoids maintained growth for at least 2 passages, indicating the presence of KRAS-activated tumor cells. Scale bar = 500 μm.
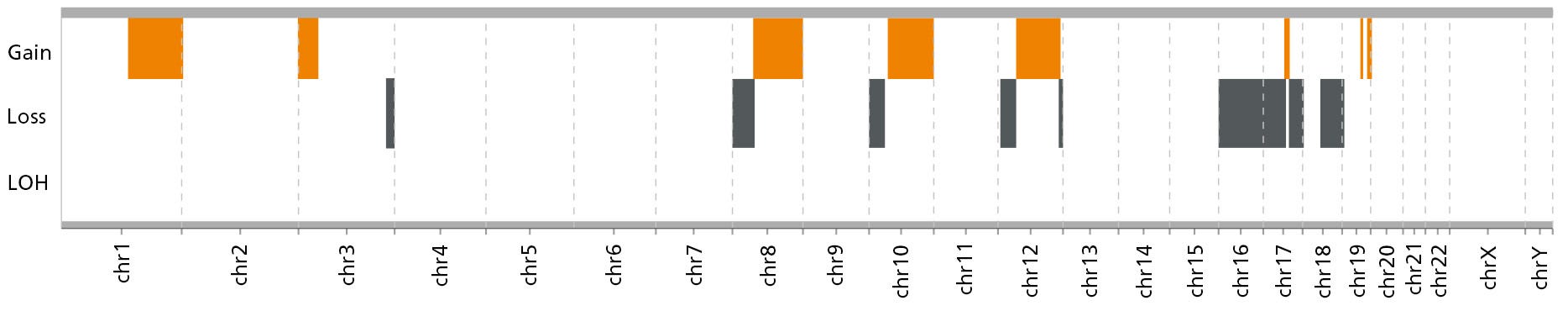
Figure 9. Organoids Can Be Established from Cryopreserved PDAC Cells Using PancreaCult™ (Human)
Mutational profile of organoids established and expanded in PancreaCult™ (Human) (Low O2, no EGF). Orange areas indicate areas of gains (top row) and grey areas indicate areas of losses (middle row) in the indicated chromosomes. There is a lack of high certainty loss of heterozygosity (LOH, bottom row). Microarray analysis was performed with Illumina iScan on the Global Diversity Array with Cytogenetics-8 (v1.0). CNVs (gene copy number variations) were called using the MoChA software tool for mosaic chromosomal alterations detection and analysis, MoChA, with human genome hg38 used as a reference.
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (6)
Related Products
-
 STEMdiff™ Pancreatic Progenitor Kit
STEMdiff™ Pancreatic Progenitor KitSerum-free medium for the differentiation of human ES and iPS cells to pancreatic progenitor cells
-
 PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Mouse)
PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Mouse)Cell culture medium for establishment and maintenance of mouse pancreatic exocrine organoids
-
 CryoStor® CS10
CryoStor® CS10Animal component-free, defined cryopreservation medium with 10% DMSO
-
 Mouse Pancreatic Organoids
Mouse Pancreatic OrganoidsCryopreserved mouse pancreatic exocrine organoids for establishment of organoid cultures
Item added to your cart

PancreaCult™ Organoid Media (Human)
Legal Statement:
This product was developed under a license to intellectual property owned by Hubrecht Organoid Technology (HUB). This product is sold for research use only. Purchase of this product does not include the right to use it for drug screening aiming for commercial gain, equipment validation, biobanking, or for other commercial purposes. Purchasers wishing to use the product for purposes other than basic research use should contact HUB at www.huborganoids.nl to obtain a further license. Purchasers may apply for a License from HUB, which will not be unreasonably withheld by HUB.
Quality Statement:
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.






