Efficient Blood Sample Processing
Tips and Tools for Red Blood Cell Depletion and Cell Isolation from Blood Samples
Considerations for Efficient Blood Sample Processing

Laboratory work is very demanding and efficiency is key to getting the most out of your day. This applies to all aspects of lab work, including processing blood samples to isolate cells. A series of changes to improve efficiency, no matter how small they might seem, if applied to frequently performed processes and tasks, can lead to significant gains in productivity.
To assess whether you are using technology that fits your need for efficient blood sample processing, ask yourself the following questions:
- How long does it take you to process blood samples to obtain cells? How can you minimize the time required by staff, so they can achieve more?
- Does your current method result in contaminants, such as red blood cells or platelets? Do they interfere with your downstream analysis?
- How easy is it to introduce errors during the protocol and what would these errors potentially cost you?
- How have you minimized and optimized the cost of your reagents?
- Have you considered using automation to streamline the process, reduce hands-on time by staff, and achieve consistency?
About Cost-Effectiveness
In some cases it may appear that using the most inexpensive reagents will be the most cost-effective solution. However, to determine the real cost of a specific technique it is also important to consider indirect costs such as technologist time, staff training time, user-to-user variability, and expenses associated with increased turnaround time.
To help laboratories work efficiently our scientists have developed technologies such as EasySep™ Direct, RosetteSep™, and SepMate™. Below we discuss how to use these cell isolation platforms to work smarter and more efficiently in the lab.
Rethinking PBMC Isolation
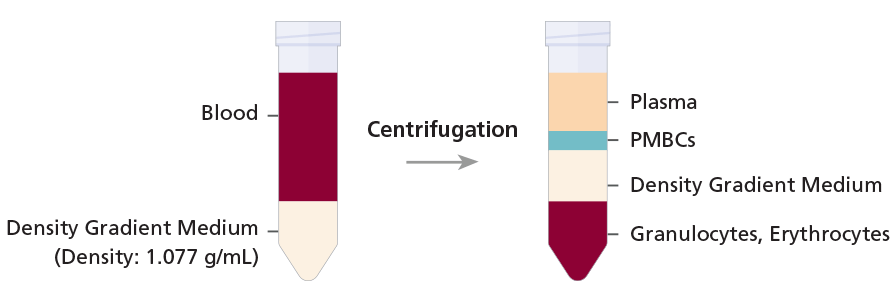
It is very common for labs to use density gradient centrifugation to process blood samples and obtain peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The PBMCs, which consist of monocytes and lymphocytes (T and B cells), can then be used for downstream assays or for further cell subset isolation. This widely used technique employs density medium such as Ficoll®, Lymphoprep™, or Lympholyte® and takes advantage of the differences in density to isolate PBMCs.
Advantages to using the density gradient method to isolate PBMCs include the low cost of the density gradient media, lack of specialized equipment, and ease of introduction to any lab.
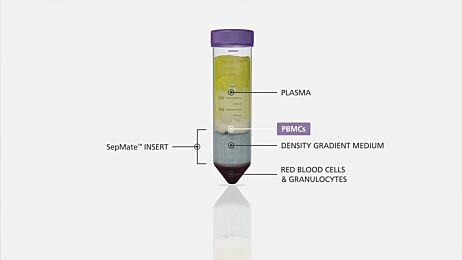
Whole blood is first diluted with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then carefully layered over the density gradient medium. After centrifugation PBMCs are collected from the density gradient medium and plasma interface
Watch a video on how to isolate PBMCs using density gradient centrifugation>
The Problem with Density Gradient Centrifugation
There are also some key disadvantages to using density gradient centrifugation to isolate PBMCs.
- It is time-consuming, laborious, and cannot be automated. Isolating cells from one sample can take at least 45 minutes.
- Over time, granulocytes and red blood cells (RBCs) in blood samples change density, and granulocytes degranulate. This means that processing older blood samples (>48 hours after collection) using density gradient centrifugation may result in granulocyte and RBC contamination.
- Reducing cell contamination in older blood samples may require longer centrifugation times and an additional RBC lysis step. These extra steps mean higher costs for reagents and time.
- This method doesn’t remove platelets. Platelets can easily become activated and removing them requires additional time-consuming washing steps.
With these disadvantages in mind, is there a smarter way to isolate PBMCs? Can density gradient centrifugation be optimized, or replaced with a better method?
Two Smarter Ways to Isolate PBMCs
1. Speed Up Density Gradient Centrifugation with SepMate™
One way to speed up PBMC isolation and reduce user to user variation is with SepMate™. The insert in the SepMate™ tube allows users to quickly layer blood over the density gradient medium while preventing the layers from mixing. Centrifugation is performed for only 10 minutes with the brake on, after which isolated PBMCs are simply poured off into a fresh tube and washed.
2. Skip Centrifugation and Automate PBMC Isolation
What if you could skip centrifugation altogether and isolate PBMCs directly from blood in as little as 20 minutes? The EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit allows you to do exactly that! This kit immunomagnetically depletes RBCs, platelets, and unwanted cells in a single step without density gradient centrifugation, sedimentation, RBC lysis, or other pre-processing steps.
With immunomagnetic cell isolation PBMCs are separated based on cell surface markers rather than cell density. Therefore, using the EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit results in highly purified PBMCs and fewer contaminating cells, even when processing older blood samples. Another great advantage is the option to automate cell isolation using RoboSep™ instruments to save hands-on time, minimize sample handling, and increase sample processing throughput.

Figure 1.EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit Results in Fewer Contaminating Cells Compared to Density Gradient Centrifugation
Mononuclear cells were isolated from whole blood samples using either density gradient centrifugation or EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit. Samples isolated with EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit have fewer contaminating granulocytes. Additional analysis of cell isolations using EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit on 24-hour, 48-hour, 72-hour, and 96-hour old blood samples show lower numbers of residual granulocytes compared to cell isolations using density gradient centrifugation. See more data>
Try Efficient PBMC Isolation in Your Lab
See for yourself how EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit can improve your blood processing efficiency.
Table 1. Automated PBMC Isolation Using RoboSep™-S Reduces the Overall Cell Separation Time Compared to Density Gradient Centrifugation
| Step | Duration (minutes) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Density Gradient Centrifugation |
Manual EasySep™ Direct |
Automated EasySep™ Direct on RoboSep™-S |
|
| Preparation of tubes with density gradient medium and layering sample | 7 | - | - |
| Loading samples and reagents onto the RoboSep™-S instrument | - | - | 5 |
| Cell isolation | 45 | 20 | 30 |
| Cell collection | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Optional: Wash step to remove platelets | 15 | - | - |
| Optional: Red blood cell lysis | 15 | - | - |
| Final centrifugation step | 15 | Optional | Optional |
| Total time for cell separation | ≥ 77 Minutes | ~ 21 Minutes | ~ 36 Minutes |
| Total hands-on time | ≥ 32 Minutes | ~ 21 Minutes | ~ 6 Minutes |
Steps and approximate times to isolate monononuclear cells from whole blood samples when following using density gradient centrifugation or EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit (manual separation or automated on the RoboSep™-S). For density gradient centrifugation, additional washing steps and red blood cell lysis might be required.
How to Deplete RBCs Without Lysis
A widely used method to remove RBCs from blood samples is lysis with ammonium chloride. Homemade or commercially available ammonium chloride potassium (ACK) solutions, also known as lysis buffers, lyse the RBCs in the blood sample while leaving leukocytes intact. The resulting leukocytes are then ready for downstream assays or further cell subset isolation. The cost of the lysis buffer is low but the process is manual and difficult to automate.
In addition to lysis with ACK buffer, other methods to deplete RBCs include dextran sedimentation and hypotonic lysis.
Watch a video on how to remove RBCs using an erythrocyte aggregation agent>
Deplete RBCs Like Never Before
Instead of lysing RBCs, the EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent immunomagnetically targets RBC for depletion to rapidly isolate untouched, highly purified human leukocytes. This targeted RBC depletion based on cell surface markers is more efficient than lysis and results in fewer residual RBCs in the sample (see figure below). In addition, this method avoids exposing leukocytes to lysis buffer, which may be a concern for particular downstream assays and analyses. With an easy-to-follow protocol, depleting RBCs with the EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent can take as little as 9 minutes without automation. RBC depletion can also be automated for increased standardization and efficiency using RoboSep™ instruments.

Figure 2. EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent Provides Superior RBC Depletion Compared to Ammonium Chloride Lysis
Different types of RBC-containing samples from normal healthy donors were processed to remove RBCs by using either ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) lysis or immunomagnetic depletion with EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent. (A) The percentages of residual RBCs (Glycophorin A+ /CD45-)in various samples following use of EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent was significantly lower compared to samples treated with ammonium chloride (mean ± SD; n = 31). (B) Both RBC lysis with ammonium chloride and RBC removal using EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent resulted in an equivalent total number of white blood cells recovered from whole blood samples (mean ± SD; n = 37).
Isolate Cell Subsets Without the Need to Isolate PBMCs First
To obtain a specific cell subset from whole blood, it is very common to first process blood with density gradient centrifugation to obtain PBMCs or use RBC lysis to obtain whole leukocytes. The resulting enriched cell preparation, which contains various cell types, can then be further processed to isolate the desired cell subsets. Cell separation technologies like EasySep™ Direct and allow you to isolate specific cell subsets directly from whole blood without needing to isolate PBMCs or whole leukocytes first. That way you can obtain your desired cell subset in a single step for smarter and more efficient blood processing.
Which Cell Isolation Technology is Best For Me?
Not sure what technology would work best to process blood samples efficiently? View this cell separation comparative table to better evaluate which of our cell separation platforms will work best for your lab.
Comparing Cell Separation Platforms from STEMCELL Technologies >
Related Resources
Isolate cells from blood
Read a detailed overview of methods to isolate different cell populations from blood samples.
Protocols for Blood Sample Preparation
- Processing a Leukopak for Downstream Cell Isolation
- How to Prepare a Buffy Coat from Whole Blood
- How to Remove Granulocytes from Old Blood Samples