EasySep™ Mouse Epithelial Cell Enrichment Kit II
Immunomagnetic negative selection kit

Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
Overview
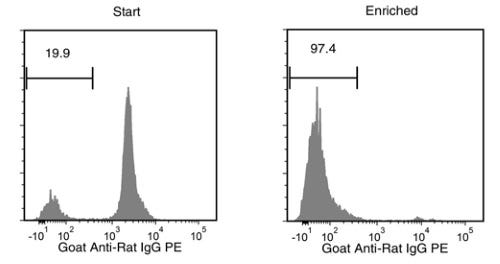
Data Figures
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (4)
Publications (2)
Abstract
Abstract
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.