EasySep™ Performance Data
Working efficiently is key to overcoming the demands of scientific research. That’s why our scientists developed EasySep™: a smarter, more efficient way to isolate cells.
EasySep™ combines the specificity of monoclonal antibodies with the simplicity of a column-free magnetic system for fast and easy isolation of highly purified cells that are ready for downstream applications. This versatile immunomagnetic cell separation technology enables positive selection, negative selection, or cell depletion. Learn how EasySep™ works >
Here are the facts about EasySep™, backed by data, so you can see the EasySep™ advantages for yourself.
Quick Cell Isolation Protocols
EasySep™ cell separation protocols are fast and easy to perform. In as little as 8 minutes (Figure 1), you can obtain highly purified cells from a variety of sample sources, including peripheral blood mononuclear cells, whole blood, leukapheresis products, bone marrow, and cord blood.
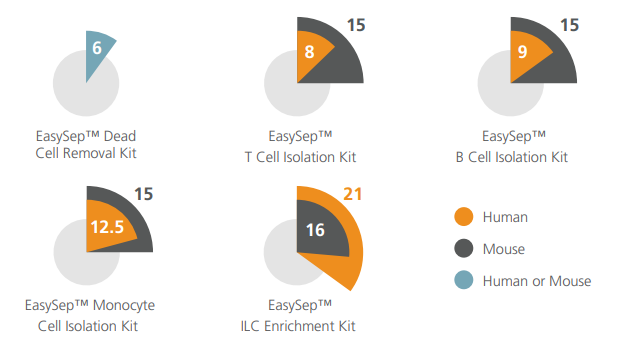
Figure 1. Cell Isolation Protocol Lengths
Typical time taken (in minutes) to isolate cells using select EasySep™ kits.
High Purity and Recovery of Isolated Cells
EasySep™ cell separation protocols are optimized so you can achieve high cell purities and recoveries.
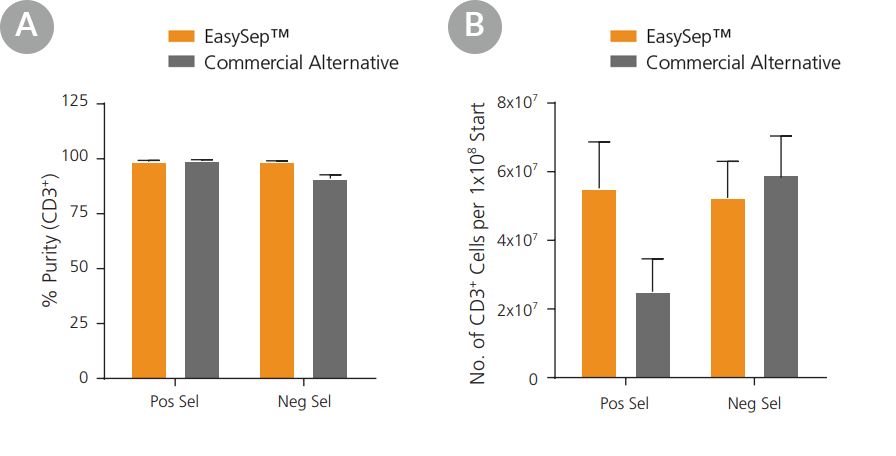
Figure 2. EasySep™ Yields Equivalent or Better Purity and Recovery of Human T Cells Compared to a Column-Based Technology
T cells were isolated by negative selection (Neg Sel) or positive selection (Pos Sel) using EasySep™ or a commercially available column-based technology. EasySep™ isolation yielded comparable or better purity (A) and recovery (B) to the commercially available system. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 3.
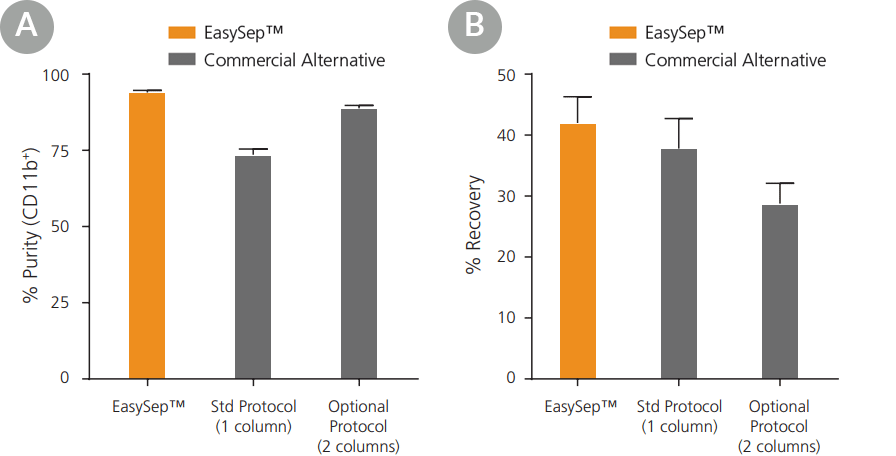
Figure 3. EasySep™ Yields Equivalent or Better Purities and Recoveries of Mouse CD11b+ Cells Compared to a Column-Based Technology
CD11b+ cells were isolated from mouse spleen by positive selection using EasySep™ or a commercially available column-based kit. The commercial alternative's protocol was followed using their standard protocol or their optional “high purity” protocol, which recommended an additional column. EasySep™ isolation yielded comparable or better (A) purity and (B) recovery. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 4 - 6.
My experience with the EasySep™ was seamless. The protocol is simple & quick, almost too easy, and has allowed me to successfully isolate my cells of interest with high purity. This gives me extra time to do other experiments and confidence in my data.
I do not have experience with other cell isolation products but I have no need to look elsewhere now as the EasySep™ is simple and does the job to perfection!
Matthew Cormier, PhD Candidate
High Cell Viability Following Cell Separation
EasySep™ allows you to get to your downstream experiments quickly, without extended manipulation of your sample. With the simple, stress-free EasySep™ protocol, cells remain highly viable after separation (Figure 4).
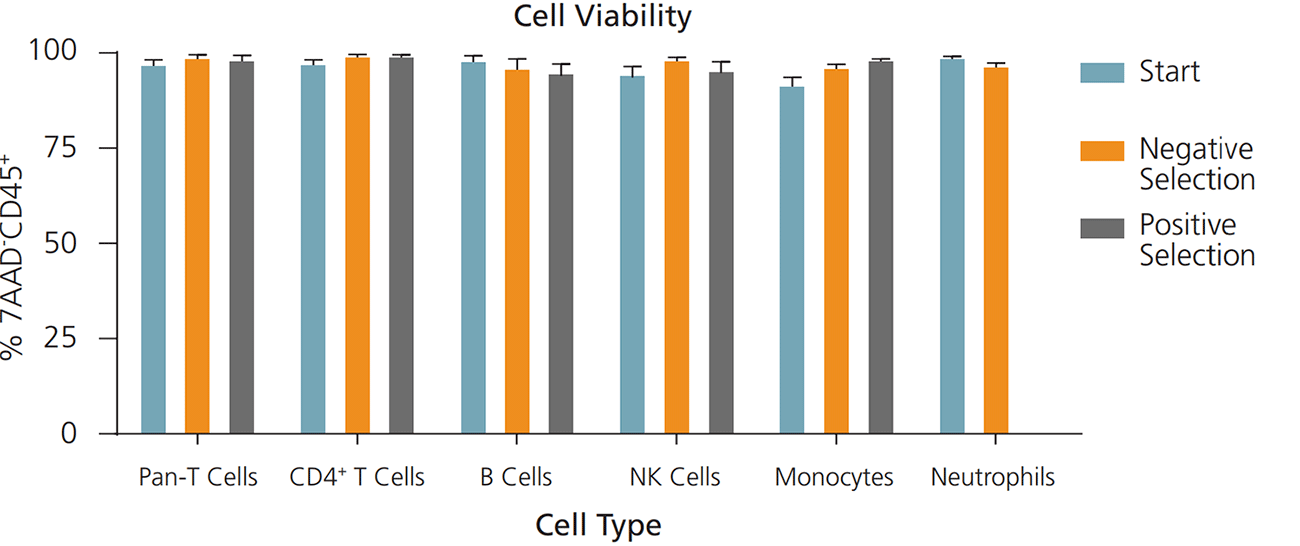
Figure 4. Cells Isolated Using EasySep™ Show Comparable Viability to Starting Samples
Immune cells were isolated from processed leukapheresis or peripheral blood samples using EasySep™ positive selection or negative selection kits. Pre- and post-isolation samples were stained with the cell viability dye 7-AAD and appropriate cell surface markers, and were assessed by flow cytometry. Cells isolated using EasySep™ showed no significant decrease in viability compared to the starting samples. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 3 - 7.
Compatible with Gene Expression Profiling Assays
Pre-enriching your samples with EasySep™ can make your next-generation sequencing workflow more efficient by improving the sequencing coverage in your cells of interest, saving you time and money.
Cells isolated using EasySep™ kits are fully compatible with next-generation sequencing workflows including library preparation, amplification, and sequencing, resulting in high-quality reads (Table 1). Gene expression profiles of CD4+ T cells isolated using EasySep™ are similar to the PBMC control (Table 1, Figure 5), indicating that EasySep™ cell isolation protocols do not introduce artifacts that affect gene expression profiles.
Table 1. Using the 10x Genomics Chromium™ Platform to Compare Single-Cell Gene Expression Profiles of EasySep™- Isolated CD4+ Cells to PBMC Controls
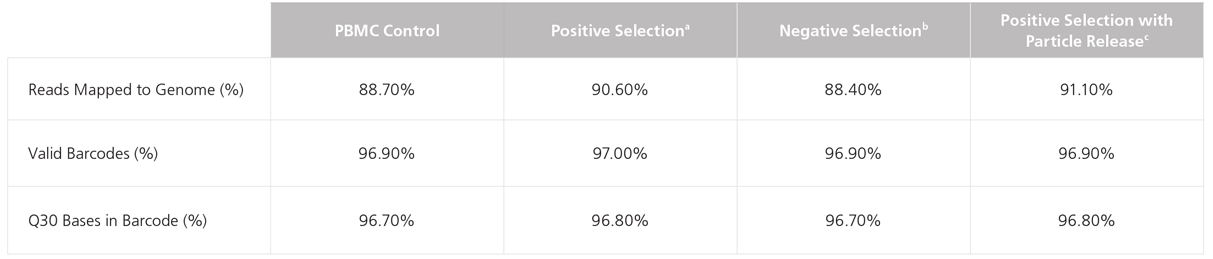
Human CD4+ cells were isolated by negative selection or positive selection using a variety of EasySep™ kits containing different types of magnetic particles:
aEasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™
bEasySep™ D Magnetic Particles
cEasySep™ Releasable RapidSpheres™
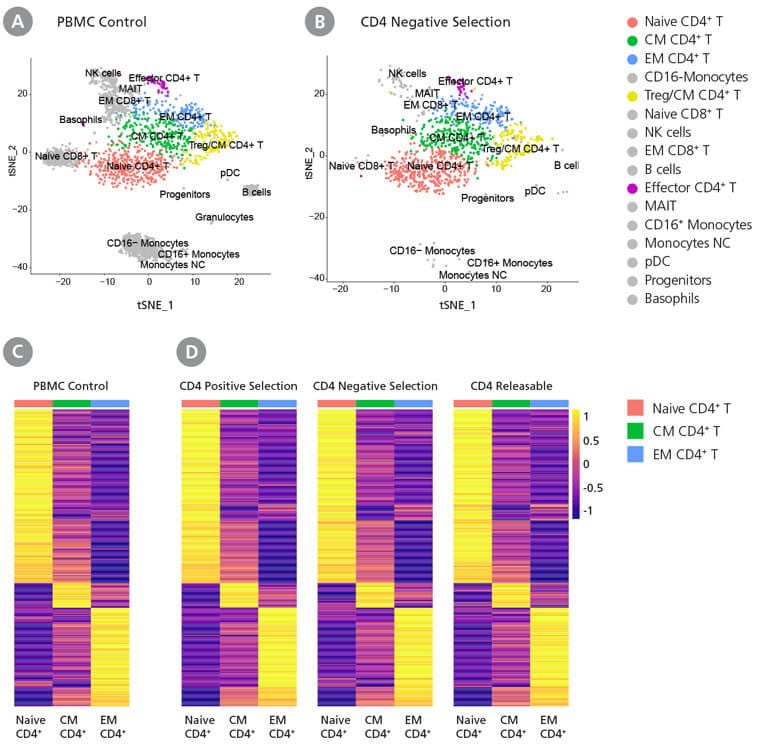
Figure 5. Gene Expression Profiles of EasySep™-Isolated CD4+ T Cells Are Similar to PBMC Control
(A,B) tSNE plots were generated using data from (A) PBMC control or (B) cells isolated using the EasySep™ Human CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19052). CD4+ T cell clusters are colored as indicated in the legend. (C,D) 500 genes were selected from a previously published list of CD4+ T cell signature markers (Zhang et al., 2018). Expression heatmaps were generated for CD4+ cells from (C) PBMC control and (D) cells isolated using the EasySep™ Human CD4 Positive Selection Kit II (Catalog #17852), EasySep™ Human CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19052), or the EasySep™ Release Human CD4 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #17752). The average expression was calculated within each sample for three CD4+ T cell clusters identified by Seurat (naïve, central memory, and effector memory CD4 T+ cells).
Isolated Cells Respond Appropriately to Stimuli
Cells isolated using EasySep™ are functional and respond appropriately to a variety of stimuli (Figures 6 and 7): stimulated cells show an activated phenotype and produce appropriate cytokines, while isolated cells remain unactivated in the absence of stimulation.
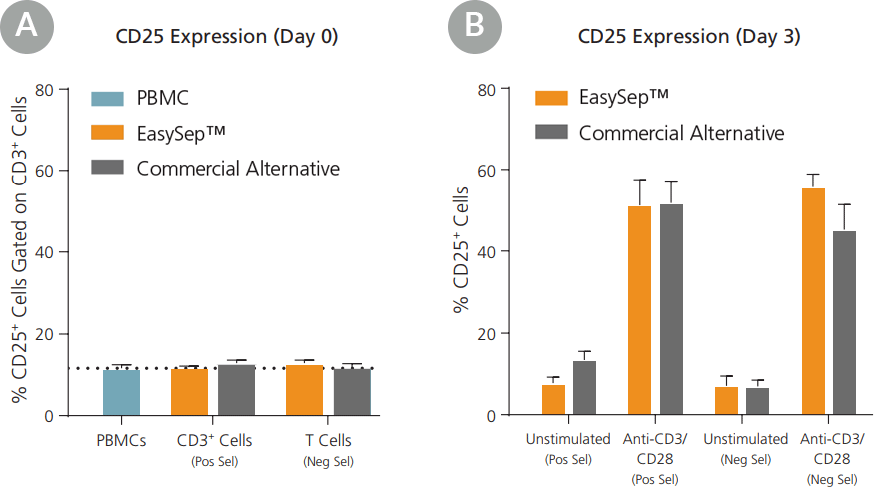
Figure 6. T Cells Isolated Using EasySep™ Show an Appropriate Activation Phenotype
Human T cells were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by negative selection (Neg Sel) or positive selection (Pos Sel) using EasySep™ or a commercially available column-based system. Isolated T cells were assessed for CD25 expression immediately after isolation (Day 0) and after 3 days in culture with or without anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation. (A) At Day 0, isolated T cells expressed similar levels of CD25 compared to CD3+ cells in unmanipulated PBMCs. (B) At Day 3, cells remained unactivated in the absence of stimulation, while stimulated cells expressed the activation marker CD25. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 3.
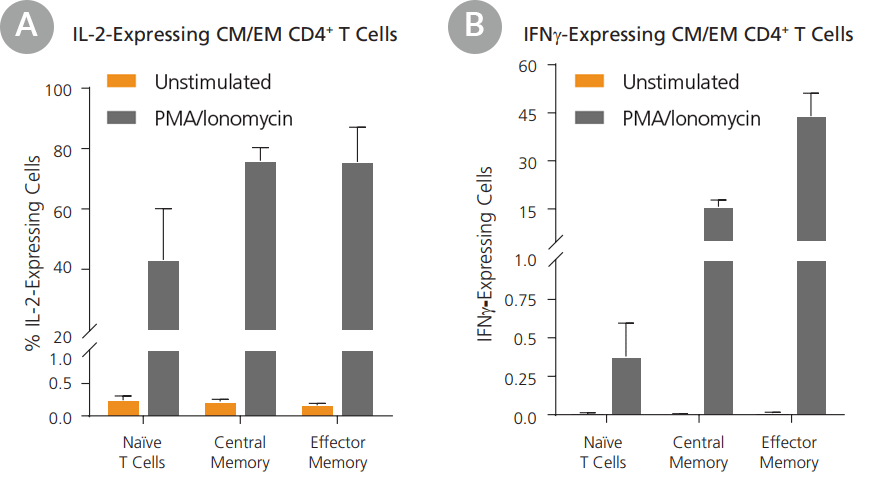
Figure 7. Central Memory and Effector Memory CD4+ T Cells Isolated Using EasySep™ Produce Cytokines When Stimulated
T cell subsets were isolated using the EasySep™ Human Central and Effector Memory CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit. Isolated cells were cultured in medium with or without PMA and ionomycin stimulation for 4 hours. T cell subsets were assessed for the expression of (A) IL-2 and (B) IFNγ by intracellular flow cytometry. In the absence of stimulation, T cell subsets produced low levels of IL-2 and IFNγ. (A) When stimulated, central memory (CM) and effector memory (EM) CD4+ T cell subsets showed significantly higher IL-2 expression compared to naïve T cells. (B) EM CD4+ T cells expressed higher levels of IFNγ than CM CD4+ T cells when stimulated. Both CM and EM CD4+ T cell subsets showed higher IFNγ expression than naïve T cells. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 3.
Carefully Optimized Cell Isolation Protocols
EasySep™ protocols and reagents are optimized to ensure robust and optimal performance across samples. Cocktails and magnetic particles are titrated to minimize non-specific binding, ensure proper cell labeling, and to avoid epitope blocking when using the recommended antibody clones for staining.
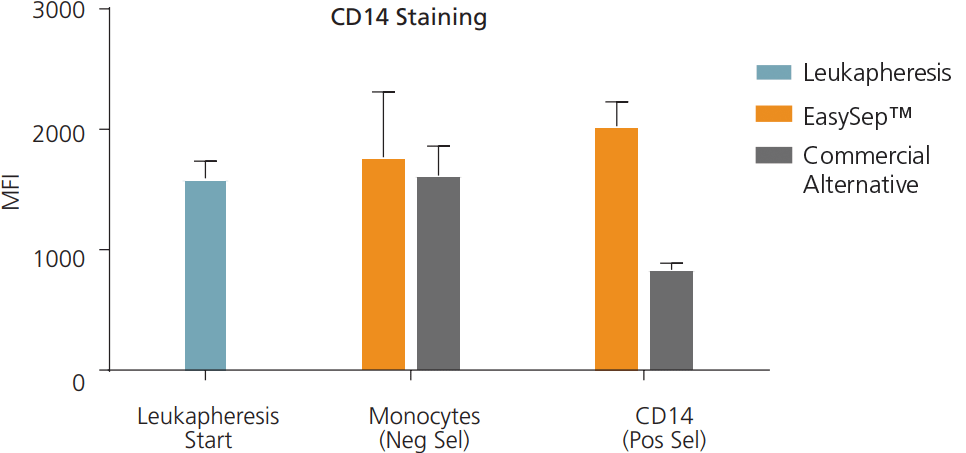
Figure 8. CD14 Epitopes Are Not Blocked Following Cell Isolation Using EasySep™
Cells were isolated by negative selection (Neg Sel) or positive selection (Pos Sel) methods using EasySep™ or a commercially available column-based technology. Isolated cells were stained using an anti-CD14 antibody (clone M5E2), and assessed by flow cytometry. EasySep™-isolated cells showed similar levels of CD14 staining (MFI) compared to unprocessed CD14+ cells (Leukapheresis Start). Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 4 - 5.
Isolated Cells Differentiate and Mature As Expected
EasySep™-isolated cells express appropriate surface markers following differentiation and maturation.
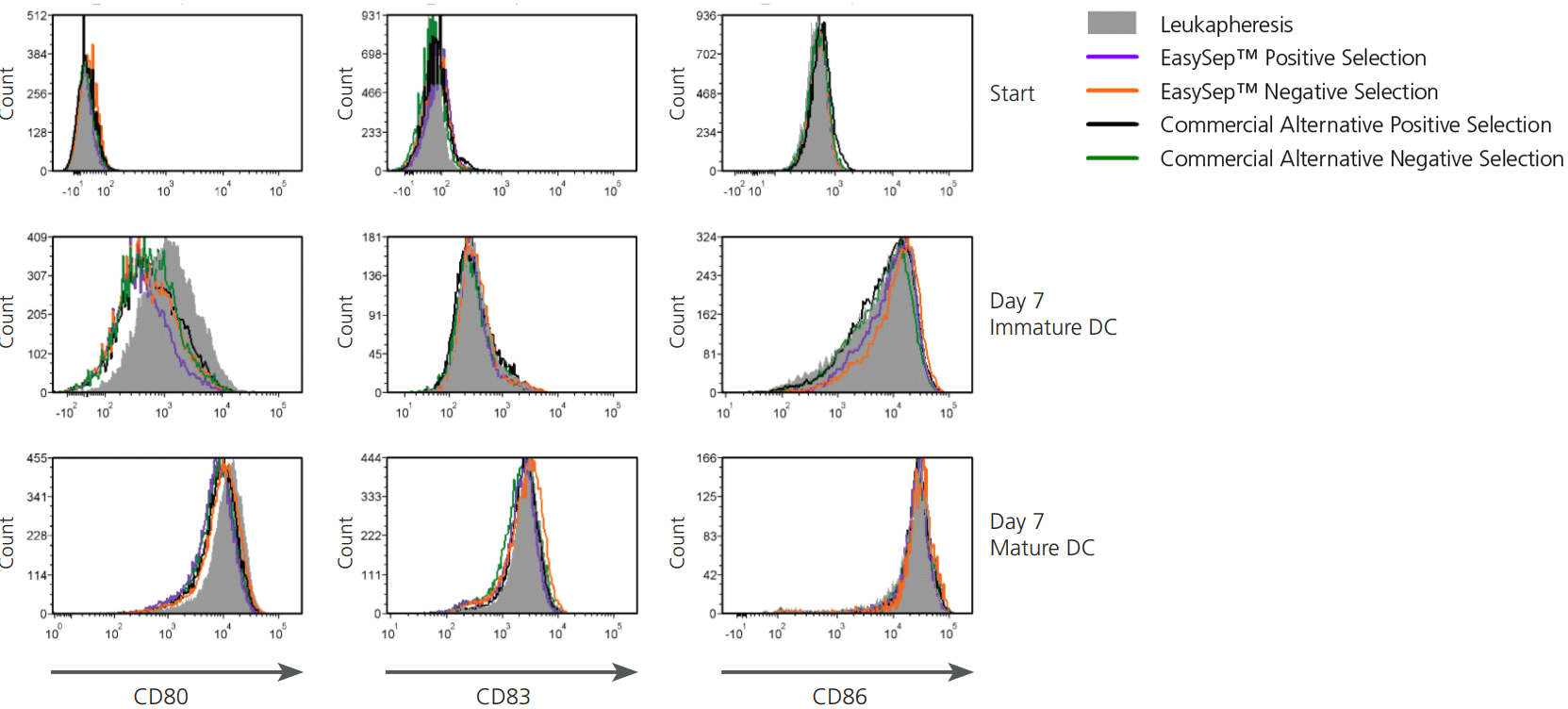
Figure 9. Monocytes Isolated Using EasySep™ Differentiate and Mature Appropriately Upon Stimulation
Human monocytes were isolated using EasySep™ or commercial alternatives and then cultured and differentiated into mature dendritic cells (DCs). On Day 0, cells from a leukapheresis sample were plated and monocytes were adherence-selected for 2 hours. Non-adherent cells were washed away and adherent cells were cultured for 7 days. On Day 5, cells were cultured with maturation supplement for 2 days (mature DCs) or without maturation supplement (immature DCs). The expression of CD80, CD83, and CD86 in immature and mature DCs was determined by flow cytometry. At Day 7, cells expressed the mature DC markers CD80, CD83, and CD86.
EasySep™ Frequently Asked Questions
How does EasySep™ work? Is it compatible with FACS? Explore these frequently asked questions and learn why scientists are switching to EasySep™.
The Ultimate Guide to Cell Separation
Learn everything you need to know about cell separation.
References
- Zhang L et al. (2018) Lineage tracking reveals dynamic relationships Of T cells in colorectal cancer. Nature 564(7735): 268-272.




