STEMdiff™ Pluripotent Stem Cell (ESC and iPSC) Differentiation
STEMdiff™ Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation Media
Reproducible Differentiation of Human ES and iPS Cells
Consistent human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) differentiation is pivotal to high-quality results. Without standardized hPSC culture conditions, even the most detailed and rigorously followed stem cell differentiation protocols may still lead to inconsistent differentiation.1,2 Use STEMdiff™—a line of culture medium kits specifically optimized for hPSC differentiation—to reproducibly differentiate multiple human embryonic stem (ES) and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell lines to 2D cell types and 3D organoid models originating from all three embryonic germ layers.
Each easy-to-use kit comes with detailed, user-friendly protocols to standardize your differentiation protocols. For gene-edited or patient-derived hPSC lines, these optimized media and protocols enable the generation of a variety of cell types with the same genotype. The STEMdiff™ family of products is part of our complete system of reagents for hPSC culture and is compatible with TeSR™ maintenance media.
Why Use STEMdiff™?
- Reduce experimental variability with formulations optimized under rigorous quality controls
- Differentiate across multiple ES and iPS cell lines
- Standardize your differentiation to cells from all three germ layers with simplified kit formats
- Generate and bank progenitor cell types for experimental flexibility or as a reliable cell source for customized downstream differentiation
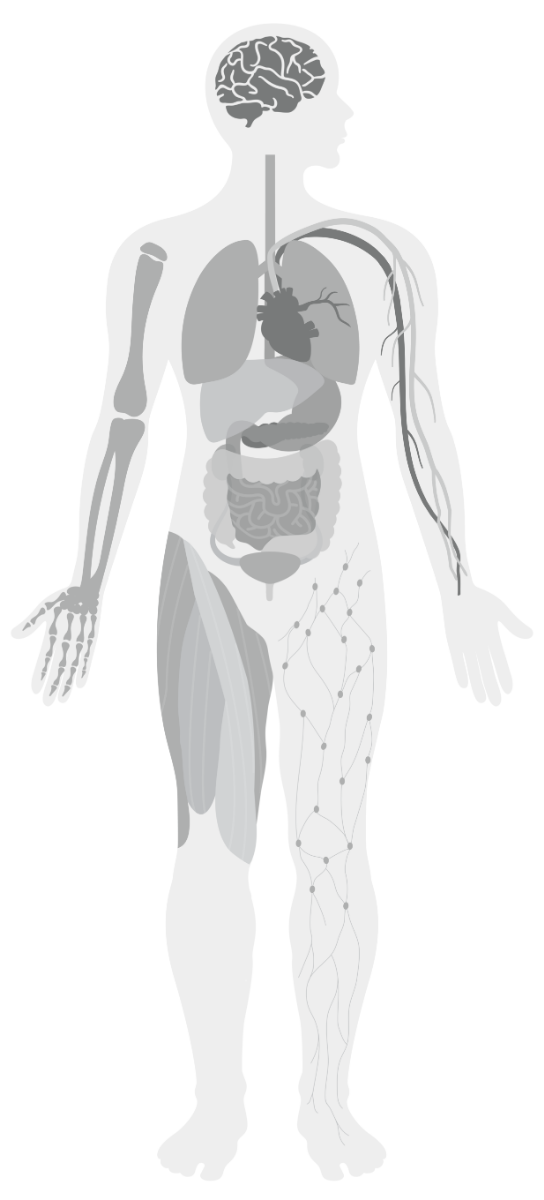
Explore STEMdiff™ Products for Different Organ Systems
Explore our collection of STEMdiff™ kits for all your hPSC differentiation needs by browsing through the interactive product explorer below. We are continually expanding our range of STEMdiff™ kits; be sure to check back periodically.
Which Organ System Would You Like to Model?
Click on a body hotspot or select an organ system below and browse the subcategories to find specific differentiation kits for your tissue of interest.
Circulatory System
Immune System
Sensory System
Stromal System
Urogenital System
- D’Amour KA et al. (2005) Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotech 23(12):1534–41
- Kattman SJ et al. (2011) Stage-specific optimization of activin/nodal and bmp signaling promotes cardiac differentiation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell lines. Cell Stem Cell 8(2): 228–40