DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium
Serum- and BPE-free medium for expansion of primary human keratinocytes
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
-
 ACCUTASE™
ACCUTASE™Cell detachment solution
-
 Hydrocortisone Stock Solution
Hydrocortisone Stock SolutionCell culture supplement
-
 D-PBS (Without Ca++ and Mg++)
D-PBS (Without Ca++ and Mg++)Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium
-
Labeling Antibodies
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
Overview
Unlike other commercial expansion media, DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium enables you to obtain > 50 population doublings of human neonatal keratinocytes and > 35 population doublings of human adult keratinocytes. With the flexibility to change the media every two days and cryopreserve proliferative cells at any passage—while maintaining their differentiation potential—you can carry out your research at your convenience. Cells expanded in this medium exhibit cobblestone morphology and express key basal cell markers (K14, p63, ITAG6, and ITGB1) representative of basal keratinocytes and are suitable for differentiation to air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures. See data.
Formulated without serum or BPE to maximize experimental reproducibility, you can confidently use keratinocytes cultured in DermaCult™ for your in vitro models to study skin and inflammatory diseases, perform irritation and corrosion assays, or to assess the efficacy of cosmetics or drugs. DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium is compatible for passaging with ACCUTASE™ (Catalog #07920) at 3 - 5 day intervals. It is also suitable for use with collagen (e.g. Catalog #04902), such as to establish keratinocyte culture from skin tissue.
Data Figures
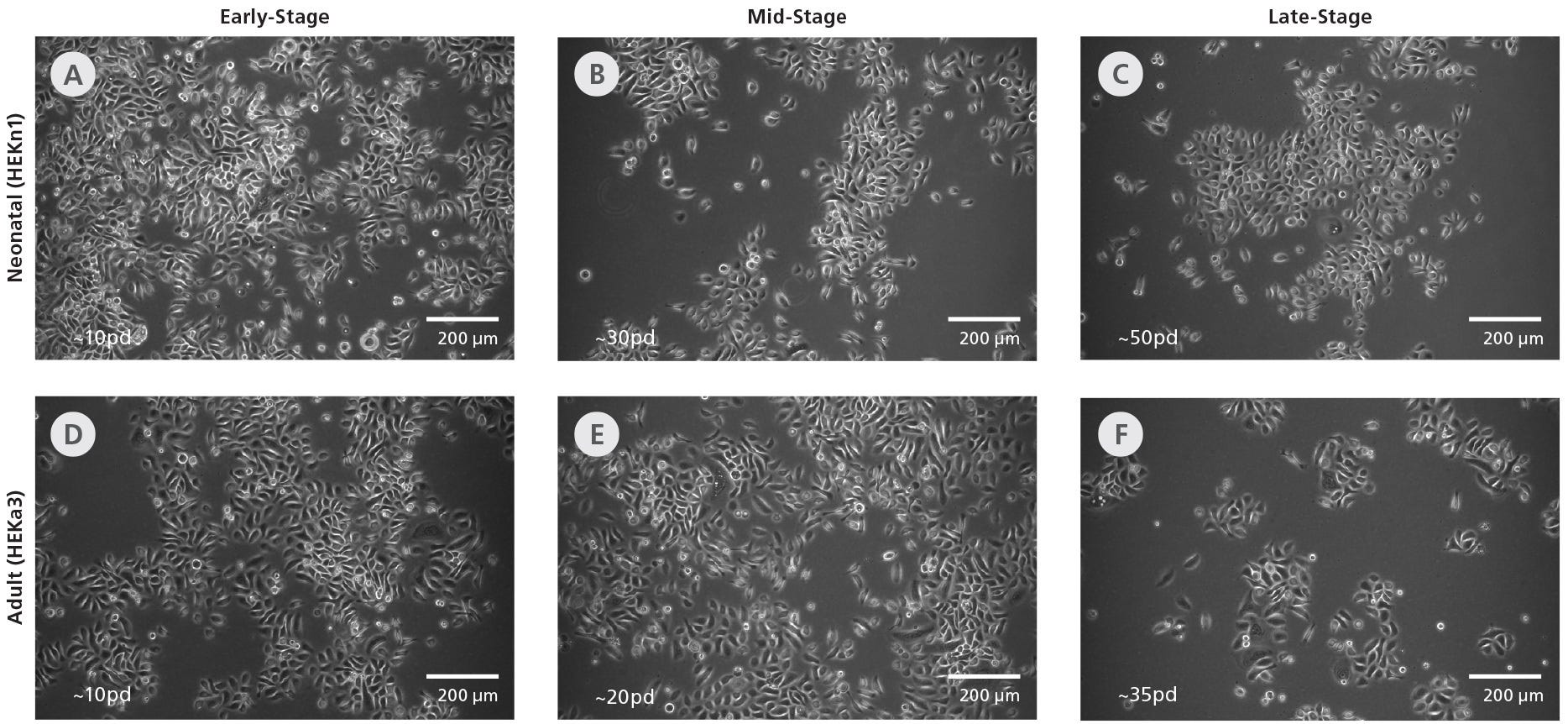
Figure 1. DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Supports Long-Term Expansion of Primary Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
(A-C) Neonatal (HEKn1) and (D-E) adult (HEKa3) human epidermal keratinocytes (HEKs) cultured long-term in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium maintain a cobblestone morphology throughout the culture period. The early-, mid-, and late-stages correspond to the number of population doublings reached. pd = population doublings. Scale bars = 200 μm. All images were taken using a 10X objective.
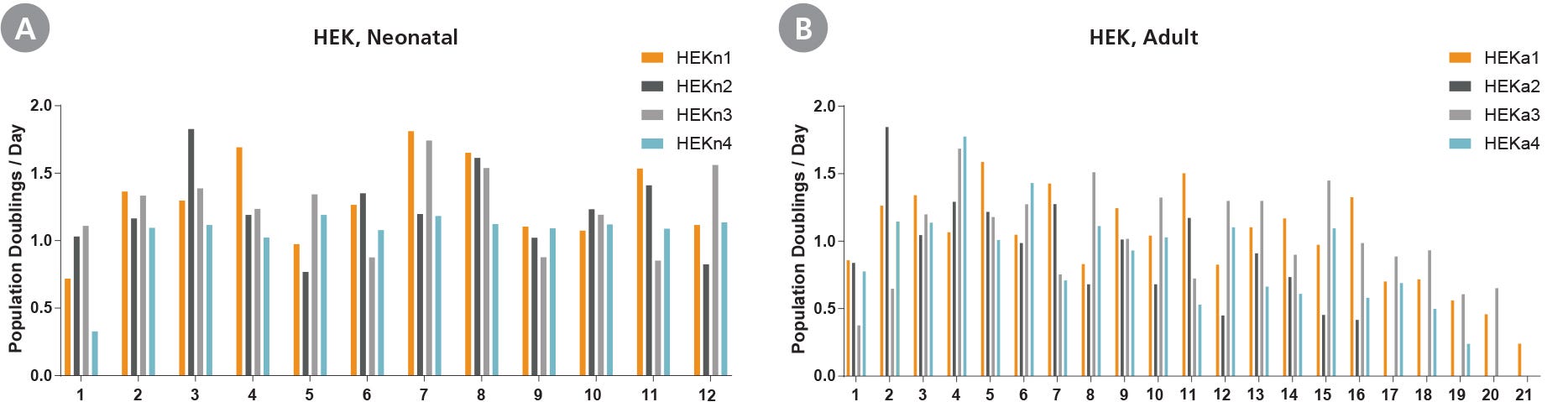
Figure 2. Primary Human Epidermal Keratinocytes Expanded in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Maintain High Growth Rates
(A) Neonatal and (B) adult HEKs cultured in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium maintain a good proliferation rate over long-term culture, as observed by the population doublings /day at each passage. The neonatal cell lines were maintained until passage 12 while the adult cell lines were maintained until senescence.
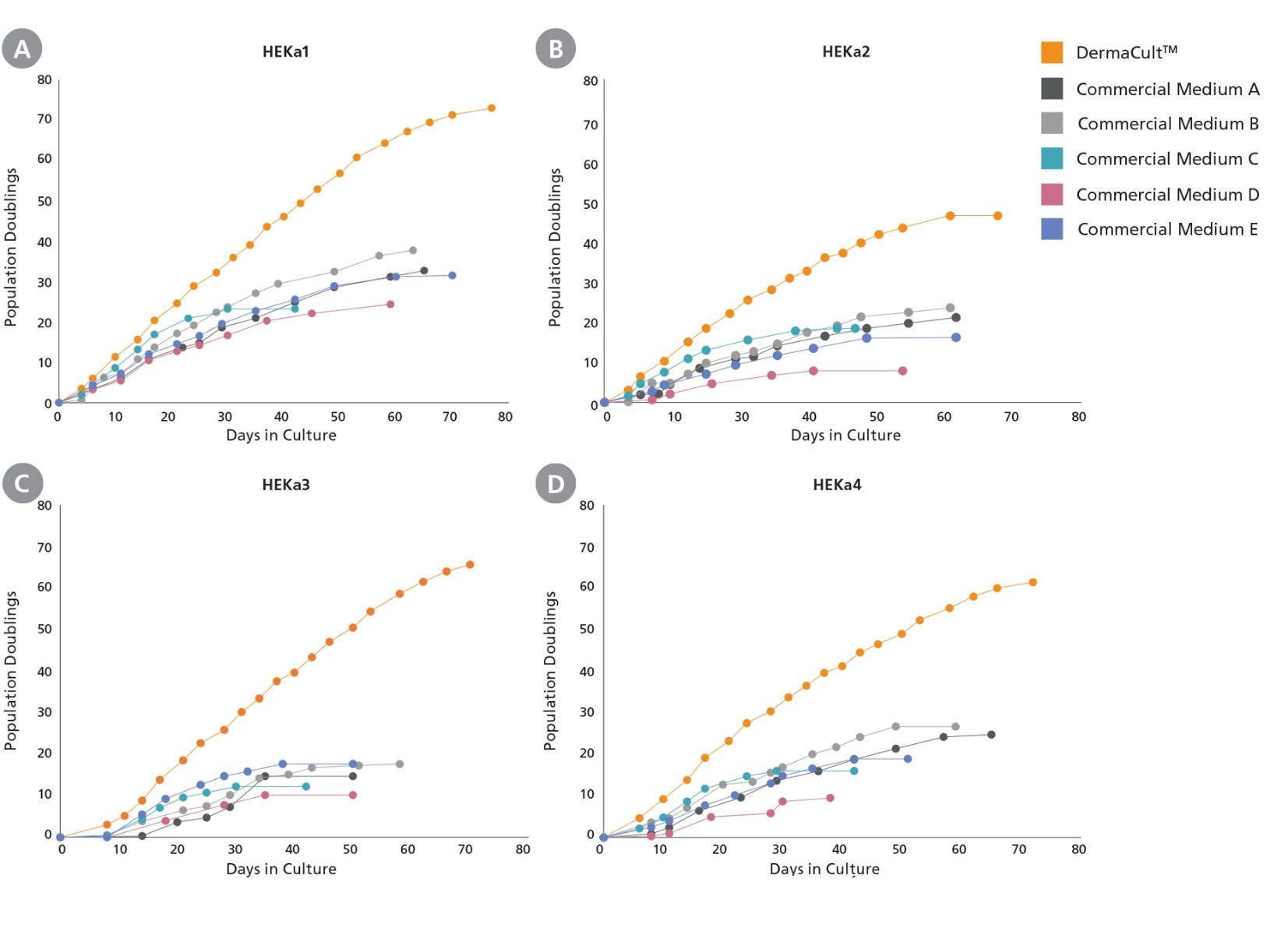
Figure 3. Primary Human Epidermal Keratinocytes Expanded in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Exhibit Increased Proliferation Rate Compared to Alternative Commercial Media
(A-D) Adult HEKs seeded and cultured in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium show an increased proliferation rate and extended longevity compared to those cultured in 5 of the leading commercial media (n=4). Growth was assessed until senescence was reached.
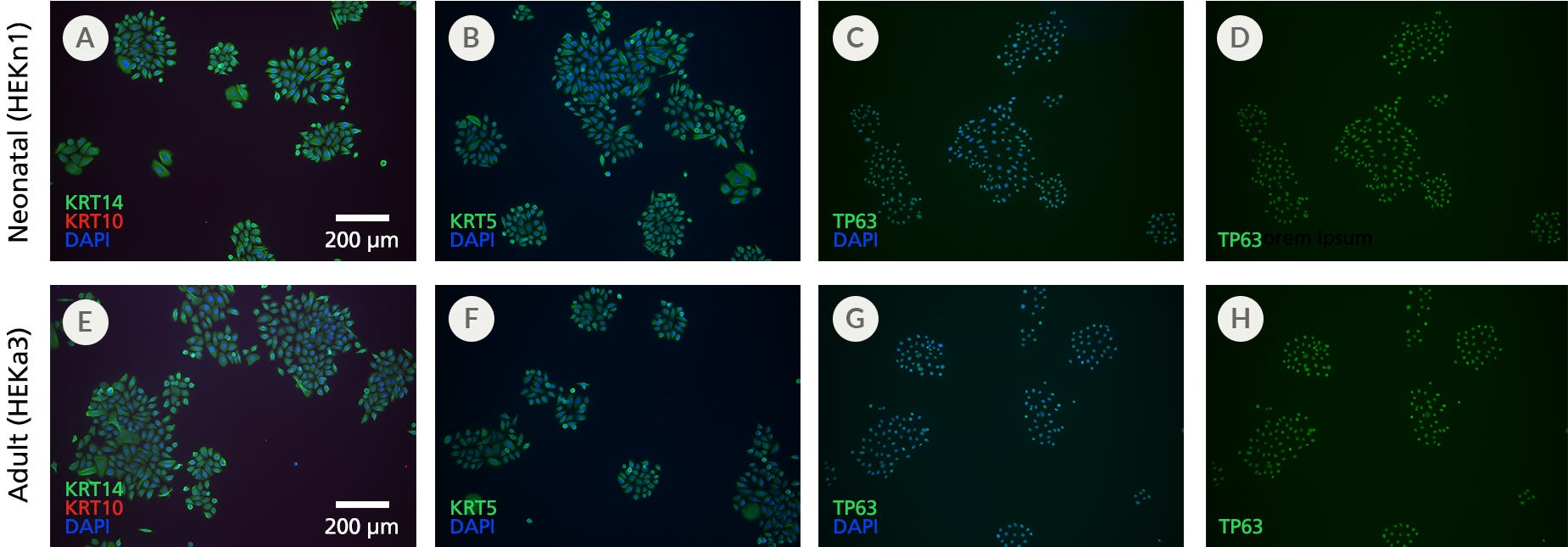
Figure 4. Primary Human Epidermal Keratinocytes Expanded in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Display Markers Characteristic of Basal Keratinocytes
(A-D) Neonatal and (E-H) adult HEKs maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium display characteristics of basal keratinocytes KRT14, KRT5, and TP63 (green) and absence of the suprabasal marker KRT10 (red), as observed through immunocytochemistry staining. Widespread co-labelling of the basal markers and the nuclear stain DAPI (blue) was observed. Scale bars = 200 μm. All images were taken using a 10X objective.
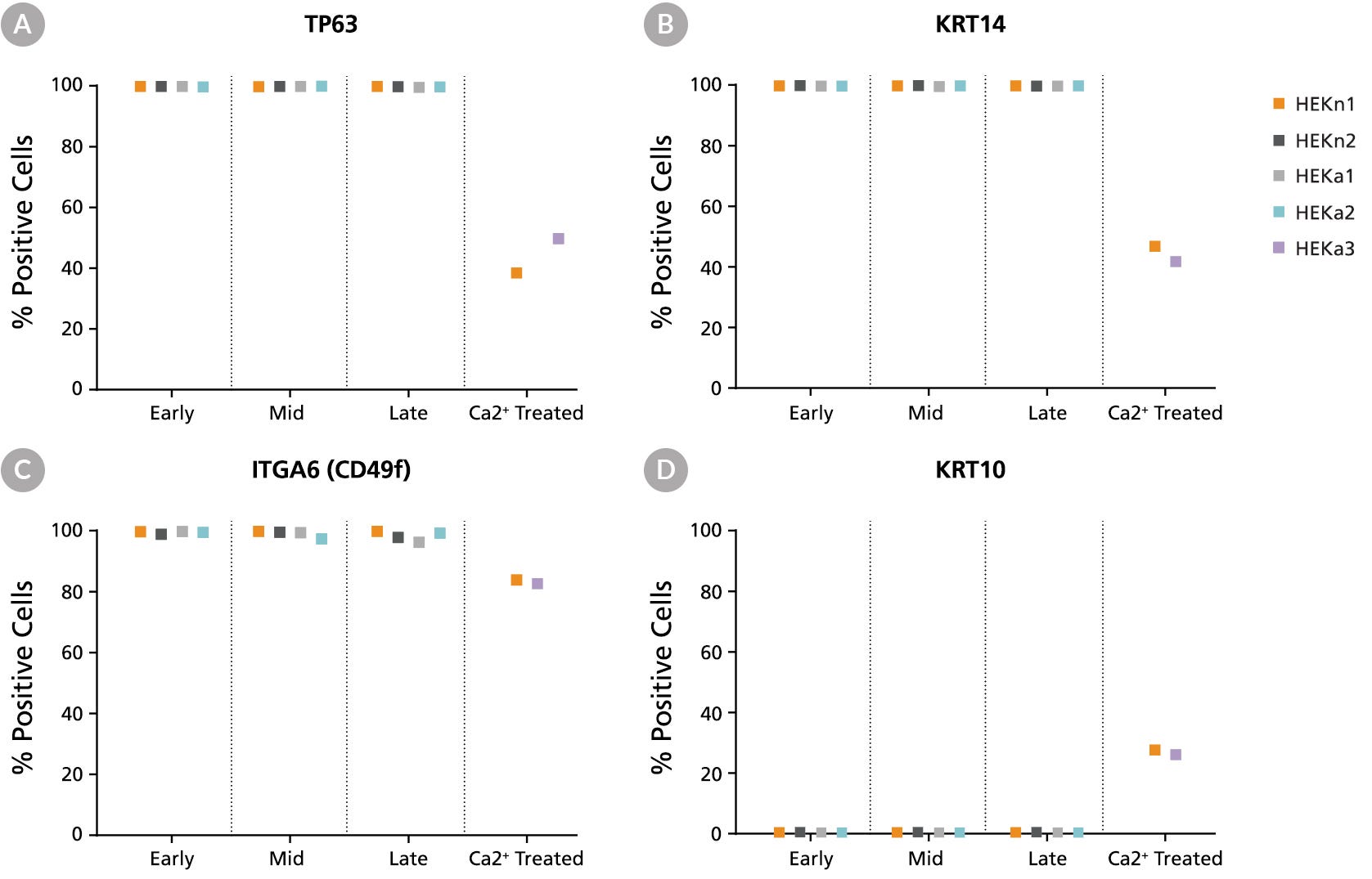
Figure 5. DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Supports Expression of Key Protein Markers
Flow cytometry analysis of 2 neonatal (HEKn1, HEKn2) and 2 adult (HEKa1, HEKa2) HEK lines maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium was performed at early-, mid-, and late-stages. Ca2+ treated (differentiated) HEKs (HEKn1, HEKa3) were included as a control. A large percentage of the cells were positive for the basal markers (A) TP63, (B) KRT14, and (C) ITGA6 (CD49f) and negative for the differentiation marker (D) KRT10. In the Ca2+ treated HEKs, there is upregulation of KRT10 and downregulation of TP63, KRT14, and ITGA6.
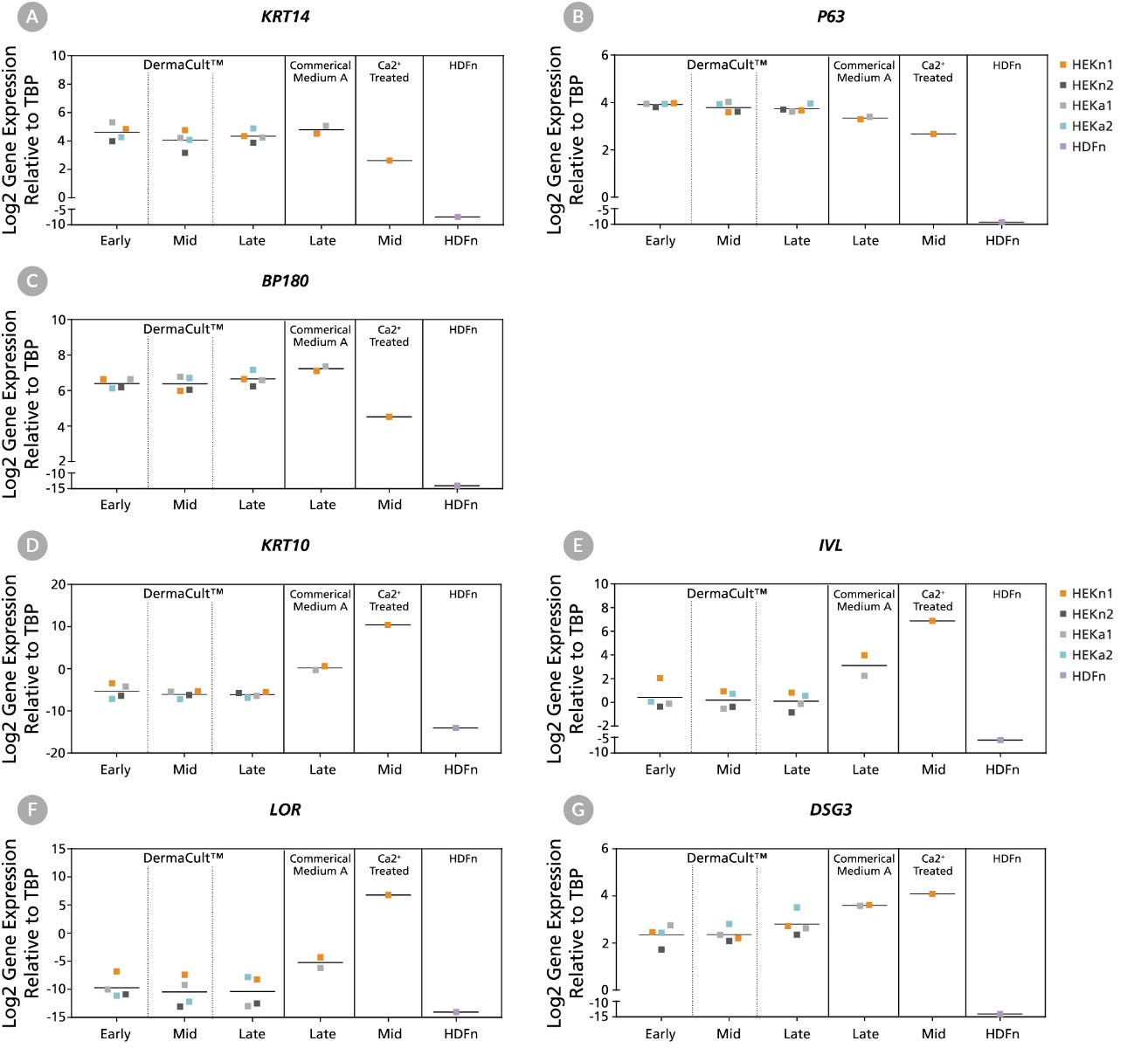
Figure 6. Human Epidermal Keratinocytes Maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Display Gene Expression Patterns Characteristic of Proliferating Keratinocytes
Gene expression profiles of 2 neonatal and 2 adult HEKs maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium analysed by RT-qPCR at early-, mid-, and late-stages shows presence of key basal keratinocyte markers. HEKs maintained in Commercial Medium A, Ca2+ treated HEKs (differentiated), and neonatal human dermal fibroblasts (HDFn) were included as controls. HEKs maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium express basal markers (A) KRT14, (B) P63, and (C) BP180. This is comparable to HEKs in Commercial Medium A and greater than the Ca2+ treated HEKs. HEKs maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium show low levels of expression of the differentiation markers (D) KRT10, (E) IVL, (F) LOR, and (G) DSG3. These markers are upregulated in the Ca2+ treated HEKs. All expression levels are normalised to the housekeeping gene TBP.
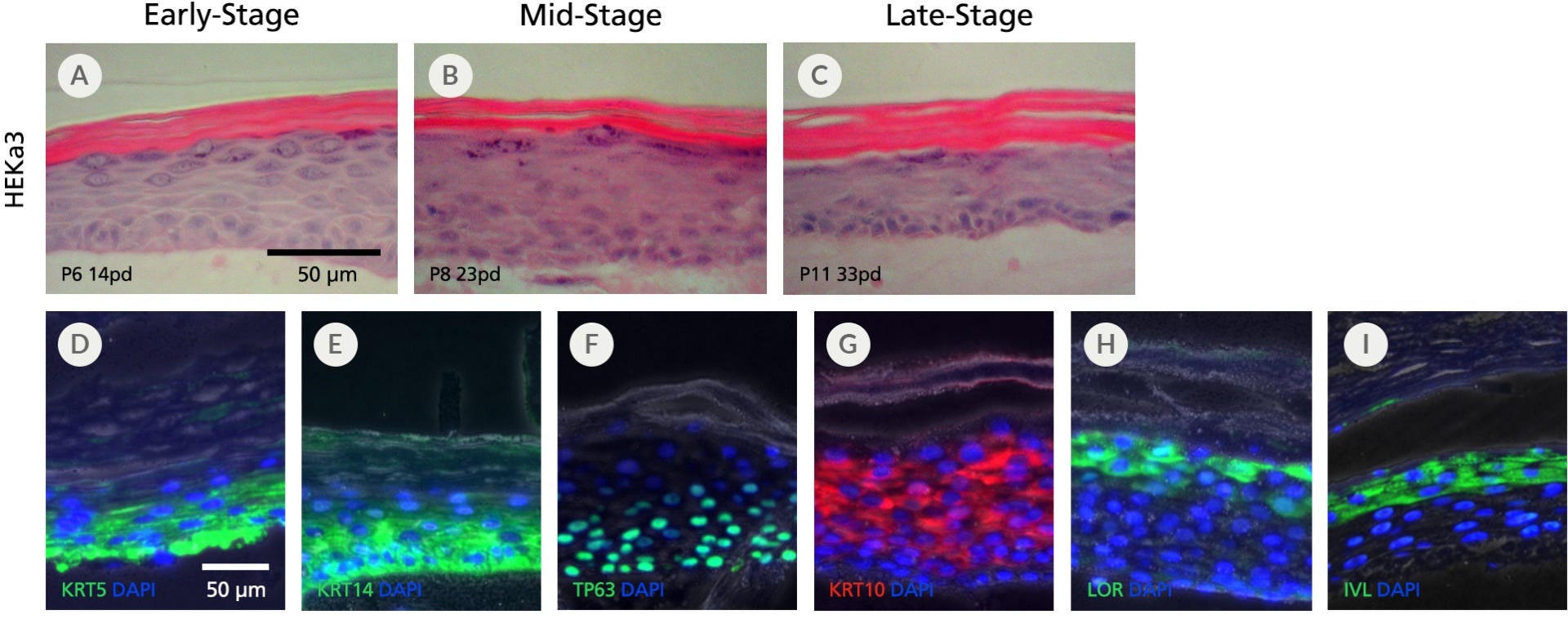
Figure 7. Human Epidermal Keratinocytes Maintained in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Differentiate at the Air-Liquid Interface
An adult keratinocyte line (HEKa3) cultured in DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium retains the ability to differentiate at the air-liquid interface (ALI) at (A) early-, (B) mid-, and (C) late-stages. H&E staining reveals a multi-layered structure with cuboidal basal cells and a clear cornified layer. The differentiated HEKs display protein markers characteristic of in vivo keratinocytes, including the expression of (D) KRT5, (E) KRT14, and (F) TP63 at the basal layers and (G) KRT10, (H) LOR, and (I) IVL at the suprabasal layers. Protein expression was visualized by immunohistochemistry. Fluorescent and phase contrast photos are overlaid. Scale bars = 50 μm. All images were taken using a 20X objective.
Gangatirkar et al (2007) Establishment of 3D organotypic cultures using human neonatal epidermal cells. Nature Protocols 2: 178:87.
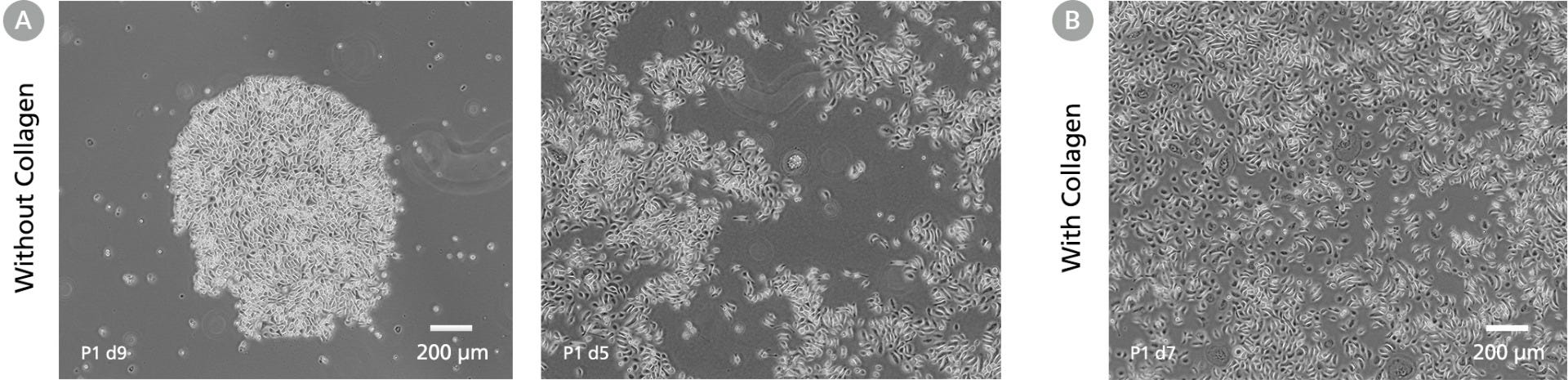
Figure 8. DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium Supports the Derivation of Human Epidermal Keratinocytes from Skin Tissue Samples
Dissociated cells from a donor skin tissue sample were seeded into DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium (A) without and (B) with collagen. Representative images show a typical cobblestone morphology in both conditions. HEKs seeded into DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium without collagen had a lower attachment (P0 d9, Figure A-left), but were able to expand and recover upon passaging (P1 d5, Figure A-right). HEKs seeded on a plate without collagen also developed more into colonies, while those on collagen were more dispersed. Scale bars = 200 μm. Images were taken using a 4X objective.
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (4)
Related Products
-
 CellAdhere™ Type I Collagen, Bovine, Soluti...
CellAdhere™ Type I Collagen, Bovine, Soluti...Purified bovine collagen for tissue engineering research, cell culture, and biochemistry
Item added to your cart

DermaCult™ Keratinocyte Expansion Medium
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.