PneumaCult™-NGEx Medium
Serum- and BPE-free culture medium for the expansion of human large airway, small airway, and nasal epithelial cells
Request Pricing
Thank you for your interest in this product. Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
-
 Animal Component-Free Cell Dissociation Kit
Animal Component-Free Cell Dissociation KitDissociation kit for human stem and progenitor cells
-
 Hydrocortisone Stock Solution
Hydrocortisone Stock SolutionCell culture supplement
-
 D-PBS (Without Ca++ and Mg++)
D-PBS (Without Ca++ and Mg++)Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium
-
Labeling Antibodies
Compatible antibodies for purity assessment of isolated cells
What Our Scientist Says
The development of our third-generation PneumaCult™ expansion medium reflects our commitment to continuous innovation and improvement. PneumaCult™-NGEx was designed to be the new Gold Standard in airway epithelial cell expansion and enable pulmonary scientists to push the boundaries of their work.

Overview
PneumaCult™-NGEx can support your cultures through extended passaging to beyond Passage 15, while maintaining the in-vivo cobblestone morphology. Importantly, airway basal cells expanded long-term in PneumaCult™-NGEx show better-conserved differentiation potential and function compared to those cultured in other commercially available expansion media. This is demonstrated by stable expression of key genes associated with basal cell maintenance and differentiation over long-term culture, such as KRT5 and p63. PneumaCult™-NGEx therefore ensures a reliable source of high-quality airway epithelial cells throughout your experiments without having to initiate new cultures over time.
Airway epithelial cells expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx are compatible with our other downstream differentiation workflows, enabling you to model the human lung at the air-liquid interface (ALI) or as organoids on a unified platform. These physiologically relevant models are valuable tools for basic respiratory research, toxicity studies, and drug development, which all begin on a foundation of robust airway epithelial cells expanded in culture.
To learn more about culturing human airway epithelial cells at the ALI or as organoids, register for our free, On-Demand Pulmonary Course, or browse our frequently asked questions on ALI and Airway Organoid Cultures.
Data Figures
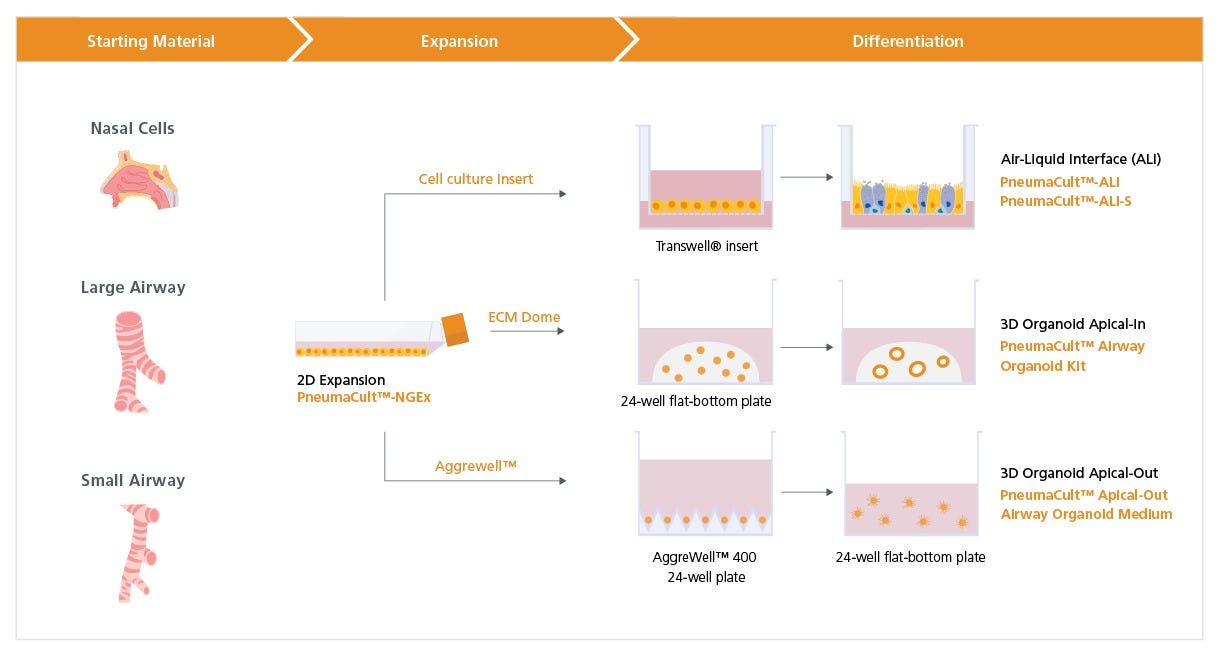
Figure 1. Overview of the PneumaCult™-NGEx Culture System
Expansion of freshly isolated or commercially available, cryopreserved human bronchial (HBECs), nasal (HNECs), and small airway epithelial cells (HSAECs) in submerged culture can be achieved using PneumaCult™-NGEx. For air-liquid interface (ALI) culture, expanded airway epithelial cells are placed on a cell culture insert. Once confluent, the cells are air-lifted by removing PneumaCult™-NGEx culture medium from both chambers. To differentiate the cells into a mature mucociliary respiratory epithelium, PneumaCult™-ALI (Catalog #05001) is added to the basal chamber for HBECs and HNECs, or PneumaCult™-ALI-S (Catalog #05050) if differentiating HSAECs. For airway organoid culture, expanded HBECs or HNECs are embedded into an extracellular matrix (ECM) dome and differentiated using the PneumaCult™ Airway Organoid Kit (Catalog #05060). Apical-out airway organoid culture, which allows access to the apical side of the airway epithelium, is achieved using PneumaCult™-NGEx-derived HBECs seeded onto an Aggrewell™ plate (Catalog #34415), followed by differentiation with PneumaCult™ Apical-Out Airway Organoid Medium (Catalog #100-0620). The compatibility of PneumaCult™-NGEx with these various differentiation workflows enables researchers to model the human lung both at the ALI and as organoids on a unified PneumaCult™ platform.
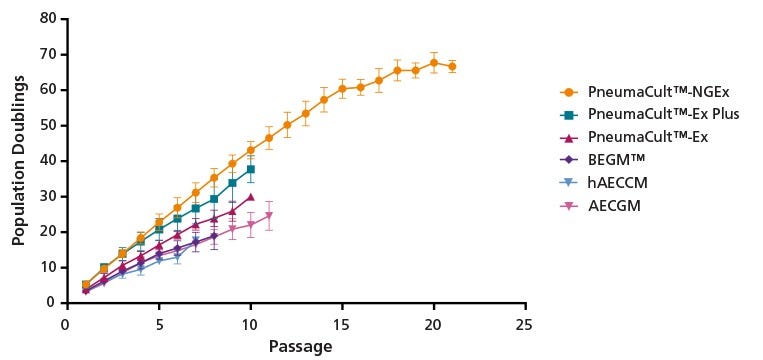
Figure 2. PneumaCult™-NGEx Supports Enhanced Expansion of HBECs Through Extended Passaging Compared to Other Expansion Media
Commercially available cryopreserved human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were expanded in the indicated expansion medium to 80% confluency and then passaged. From the initial thaw, population doublings were measured for each passage. Compared to previous generations of PneumaCult™-Ex (Catalog #05008) and -Ex Plus (Catalog #05040), and other commercially available media tested, PneumaCult™-NGEx showed a significantly higher total population doubling and was able to maintain the culture until passage 20. Each data point represents the mean ± SD (n = 4 - 6 donors). Cells expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx maintained genomic stability. As determined by microarray, no copy number variation (CNV) was observed in up to 50 population doublings (passages 13 - 15), and only two of three donors acquired 1 - 2 CNVs beyond this point (data not shown). Other commercially available expansion media tested include Lonza Bronchial Epithelial Cell Growth Medium (BEGM™), Epithelix hAEC Culture Medium (hAECCM), and PromoCell Airway Epithelial Cell Growth Medium (AECGM).

Figure 3. PneumaCult™-NGEx Enables Extended Passages Without Compromising Morphological Integrity Compared to Other Expansion Media
Representative brightfield images of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) cultured in their respective expansion media. Cobblestone morphology was observed in PneumaCult™-NGEx, and was preserved until passage 15. In contrast, other media tested maintained this morphology for fewer than 12 passages. These results indicate that HBECs cultured in PneumaCult™-NGEx can reach higher passages in long-term culture without compromising the quality of the morphology. Scale bar = 200 µm.
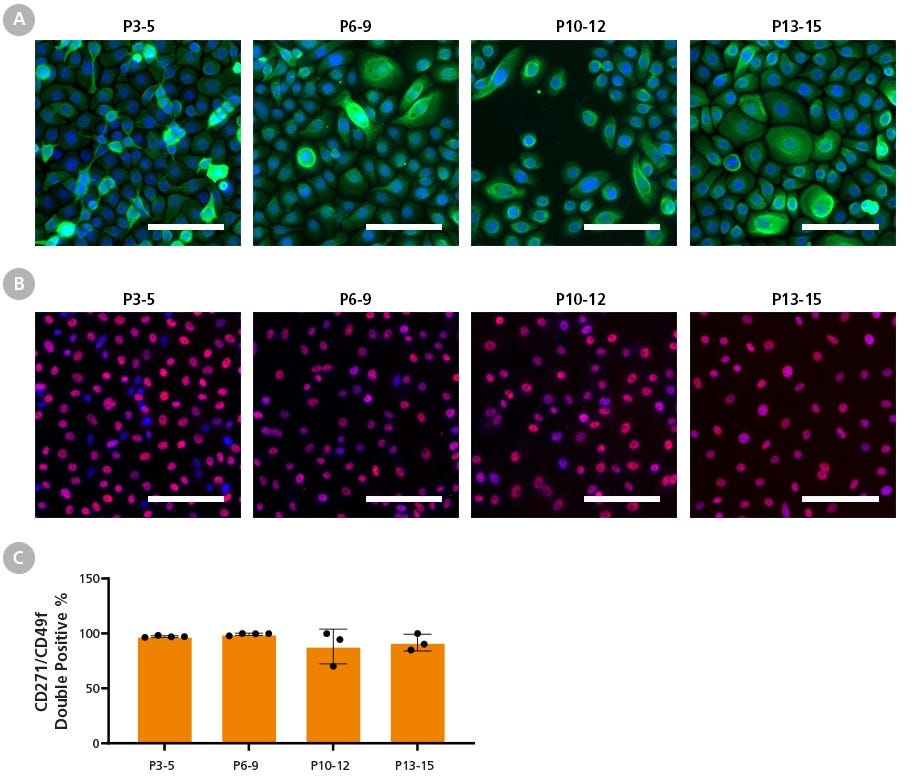
Figure 4. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Maintain Basal Cell Marker Expression Over Long-Term Passaging
Human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx until cellular senescence and stained for basal cell markers (A) KRT5 (green), (B) p63 (red), and counterstained with DAPI. Almost 100% of the cells expressed KRT5 and p63, and the expression of these markers was maintained beyond passage 13. This indicates culture stability and preserved differentiation potential over long-term culture, providing a wide experimental window. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Expression of basal cell markers CD271 and CD49f were determined by flow cytometry at regular intervals and were maintained at nearly 100% between passages 3 - 9, before slightly dropping at later passages. This indicates that HBECs expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx do not lose their basal cell identity over long-term passaging. Data represents the mean ± SD, n = 3 - 4 donors.
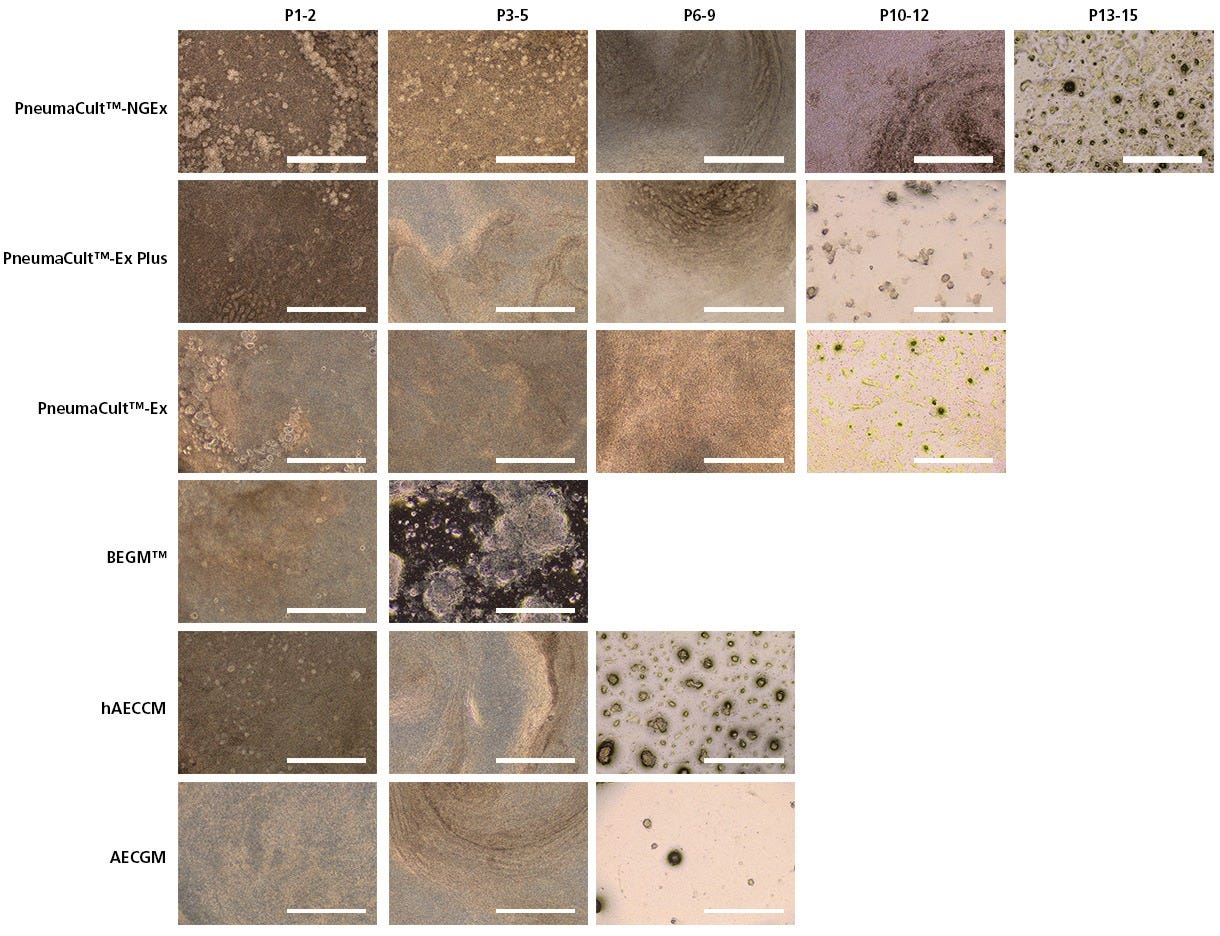
Figure 5. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Can Be Differentiated at the ALI and Exhibit Functional Barrier Characteristics Over Extended Passages
Comparative morphology of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs; top view) expanded in PneumaCult™ and other commercially available expansion media, followed by 28-day differentiation at the air-liquid interface (ALI) using PneumaCult™-ALI (Catalog #05001) and cultured until failure. Darker brown areas, homogenous cultures, and swirling patterns are indicative of a mature pseudostratified epithelium with beating cilia and mucus secretion. Poorer differentiation is marked by clumped cells, holes in the cell layer, and lighter coloration (n = 4 - 6 tested donors). Scale bar = 1000 µm. Characteristics of healthy, functional cultures are observed in NGEx-derived ALI cultures, which are maintained beyond passage 10, whereas ALI cultures expanded in other tested media start to exhibit characteristics of poor differentiation before passage 10. These findings indicate that HBECs expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx maintain their ability to differentiate at the ALI with functional barrier characteristics for an extended period, making PneumaCult™-NGEx a reliable choice for long-term airway epithelial studies.
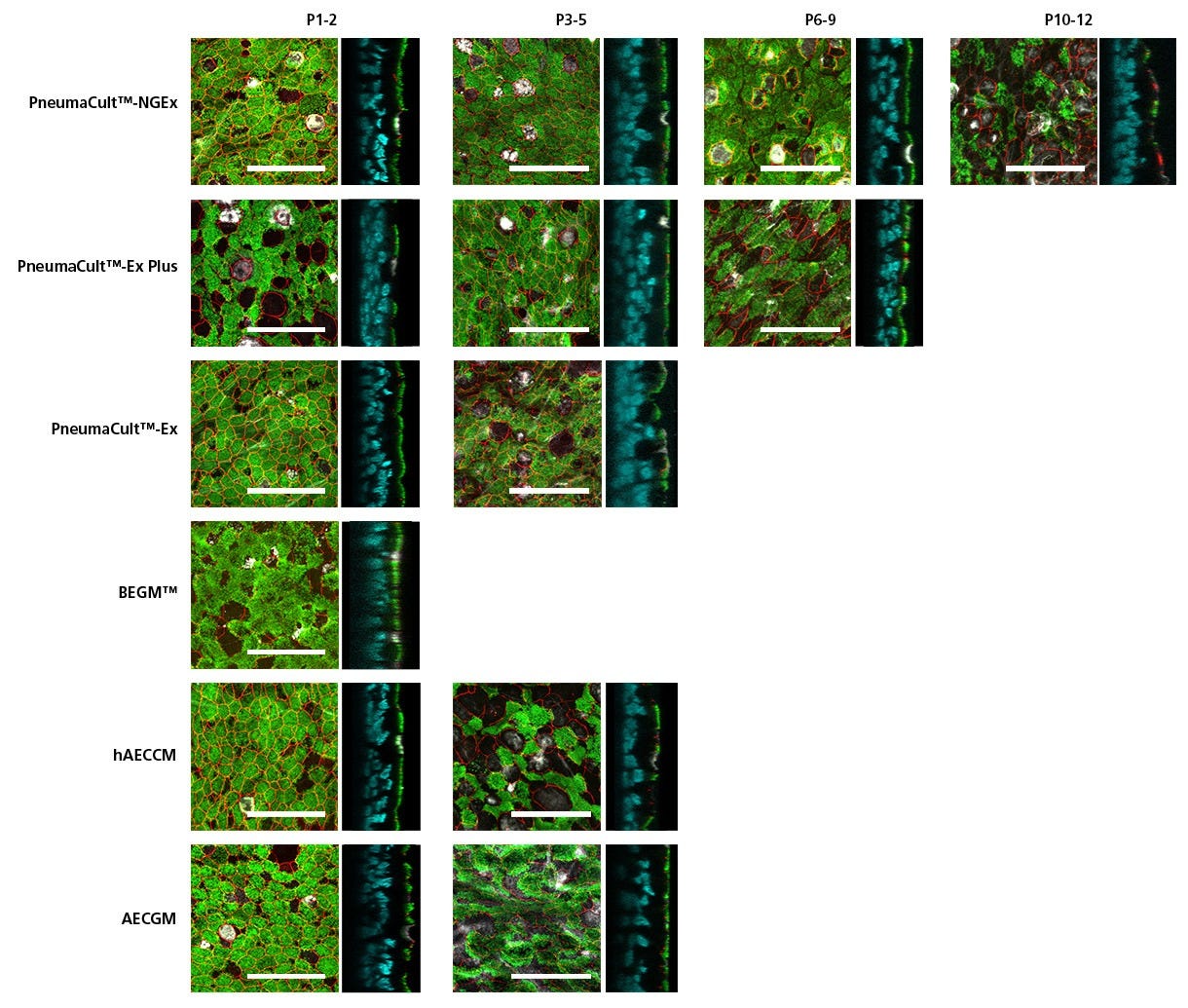
Figure 5. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Form Pseudostratified Epithelium with Expansive Cilia and Secretory Cell Expression After Differentiation with PneumaCult™-ALI
Primary human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx and other commercially available expansion media, followed by at least 28-day differentiation on cell culture inserts using PneumaCult™-ALI (Catalog #05001). Cells expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx generate a thick, pseudostratified epithelium that expresses tight-junction marker ZO-1 (red), and both ciliated and secretory cell markers—acetylated tubulin (green) and MUC5AC (white), respectively. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (cyan) and only displayed in the orthogonal slices. Notably, even after several passages, these functional markers remained expressed up to passage 12 in NGEx-derived cultures (n = 4 - 6 tested donors). Scale bar = 50 µm. HBECs cultured in PneumaCult™-NGEx can support physiologically representative morphology of the in vivo human airway with relevant marker expression and function over long-term culture, reaching twice the number of passages when compared with other commercially available media.
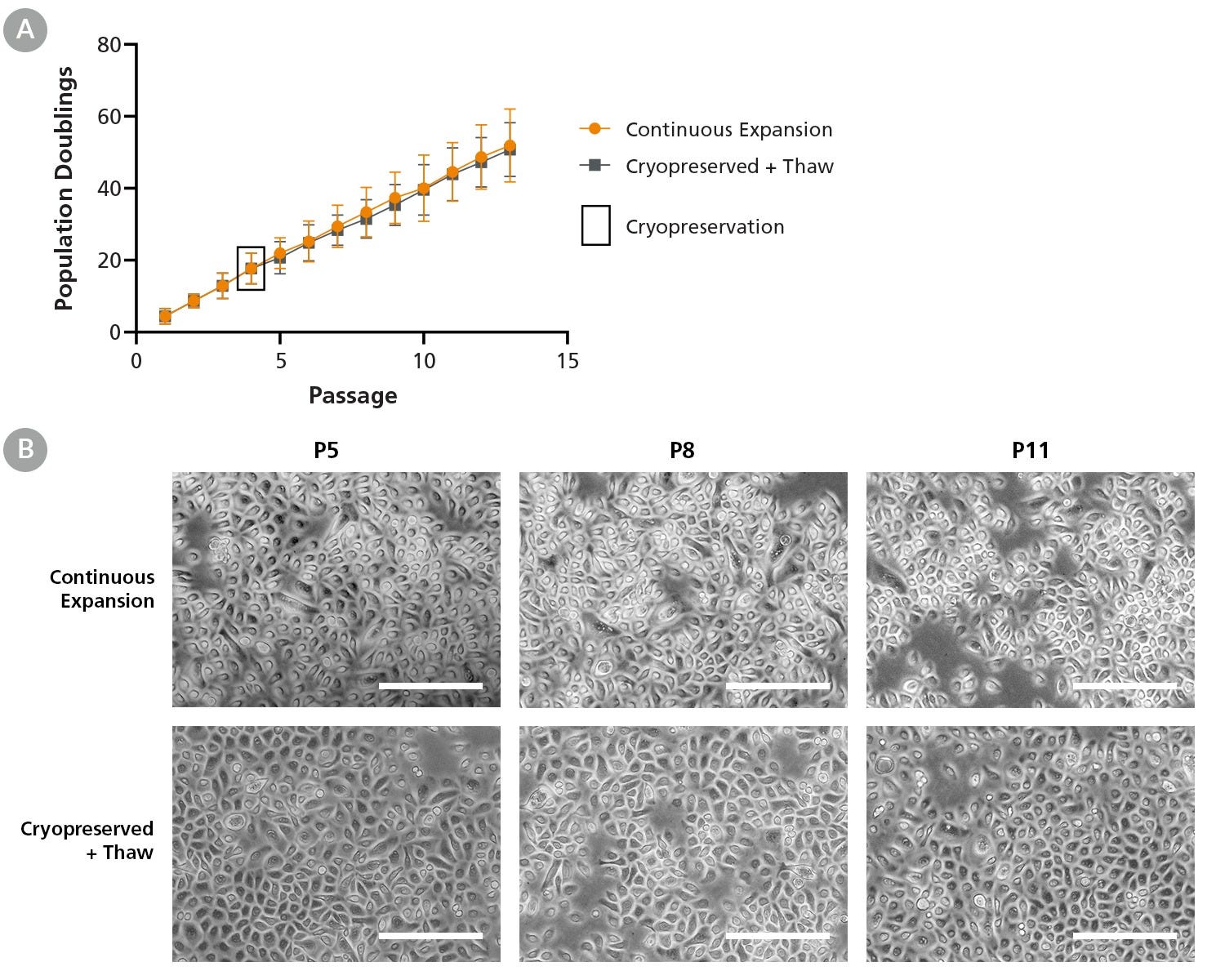
Figure 7. PneumaCult™-NGEx Supports Cryopreservation of HBECs with Identical Expansion and Morphology Before and After Thaw
Commercially available human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx and were either (A) cryopreserved after four passages, or continuously passaged. Each data point represents the mean ± SD (n = 2 donors). After thawing, cryopreserved cells were re-expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx and showed identical population doublings and (B) morphology compared to continuously expanded cells. These results indicate that HBECs expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx can be cryopreserved and successfully re-expanded while maintaining their doubling rate and morphological characteristics, even at later passages. Scale bar = 200 µm.

Figure 8. Gene Expression Analysis of HBECs Cultured in PneumaCult™-NGEx Confirms the Presence of Key Airway Cell Types During Expansion and After Differentiation
Heatmap showing changes in the RNA levels of common expansion and differentiation markers in human bronchial epithelial cell (HBEC) cultures expanded in PneumaCult™-Ex Plus (Catalog #05040) or PneumaCult™-NGEx, and differentiated with PneumaCult™-ALI (Catalog #05001). HBEC cultures were analyzed at passages 3 - 5 for both media, and at passages 10 - 12 for PneumaCult™-NGEx. Markers for ciliated, secretory, and ionocyte cells were upregulated in differentiated HBEC cultures, reflecting the in vivo human bronchial epithelium, as seen in published RNA-Seq datasets (Cordero et al., 2022 ) of non-cultured, ex vivo bronchial epithelium. This data demonstrates the transition of basal cell markers to specialized airway cell types, with PneumaCult™-NGEx supporting optimal gene expression levels that are maintained at higher passages. Columns represent the mean of 2 - 5 donors analyzed by bulk RNA-seq, and gene expression values are scaled by row.
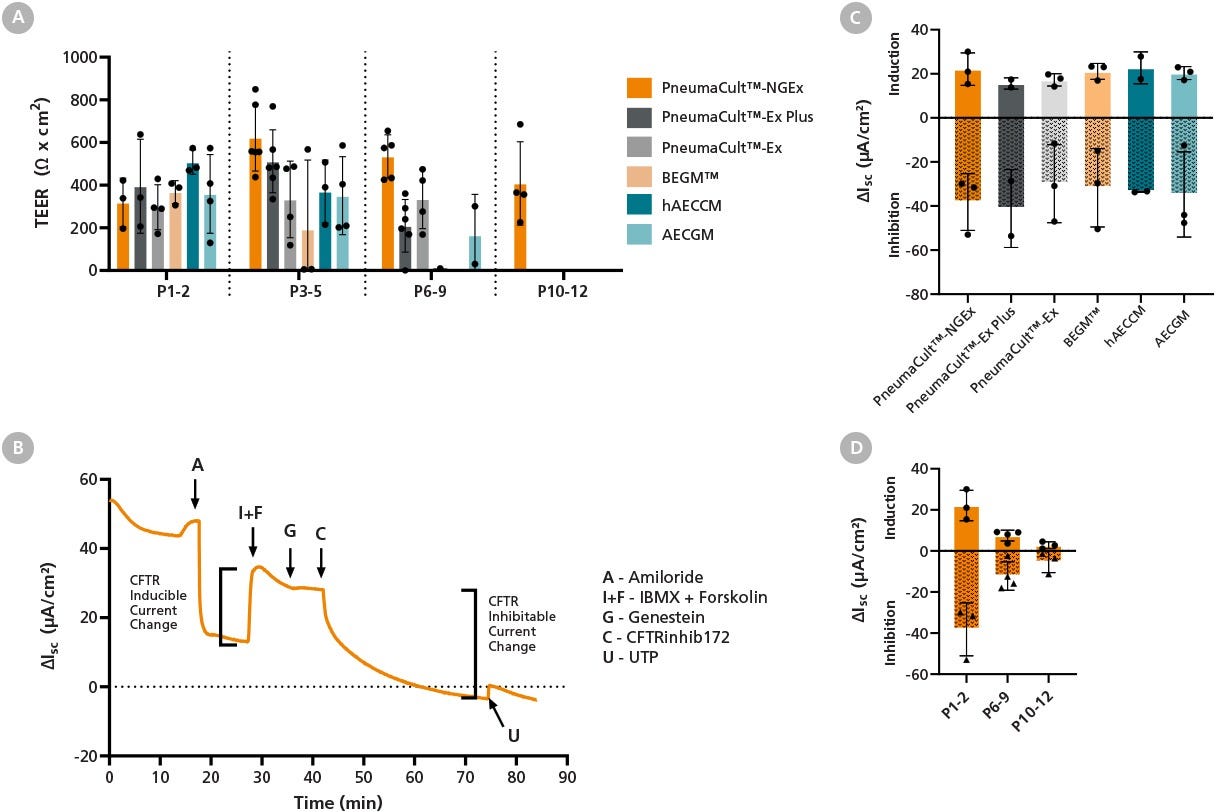
Figure 9. Expansion in PneumaCult™-NGEx Supports Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Electrophysiological Function in Differentiated ALI Cultures, Which Can Be Measured at Late Passage
(A) At lower passages, transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) is similar between PneumaCult™-NGEx, PneumaCult™-Ex Plus (Catalog #05040), and other tested expansion media. Human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx were able to maintain TEER after differentiation up to passage 12, while cultures expanded in other media lose barrier function at earlier passages. Data represents mean ± SD, n = 3 - 6 donors.
(B) Ion channel activities for air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures at 28 days post-air-lift were characterized using HBECs expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx. Cells were placed in Ussing Chambers and allowed to equilibrate to a baseline short circuit current (Isc). Cells were then challenged with epithelial sodium channel blocker (Amiloride), cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activators (IBMX + Forskolin), CFTR potentiator (Genestein), CFTR inhibitor 172 (CFTRinhib172), and then calcium-activated chloride channels activator (UTP). The change in Isc after IBMX + Forskolin addition was measured as the CFTR induction. The reduction in Isc after CFTRinhib172 addition was measured as the CFTR inhibition.
(C) CFTR induction and inhibition were measured at early passages (P1 - 2) across all tested media, with no significant differences observed (mean ± SD, n = 2 - 3 donors).
(D) In PneumaCult™-NGEx, CFTR function gradually decreased with passaging, but remained quantifiable at later passages. Data represents mean ± SD, n = 3 - 4 donors. These results demonstrate that PneumaCult™-NGEx supports the long-term expansion of HBECs while preserving epithelial barrier integrity and electrophysiological function in ALI cultures, including sustained CFTR activity at later passages.
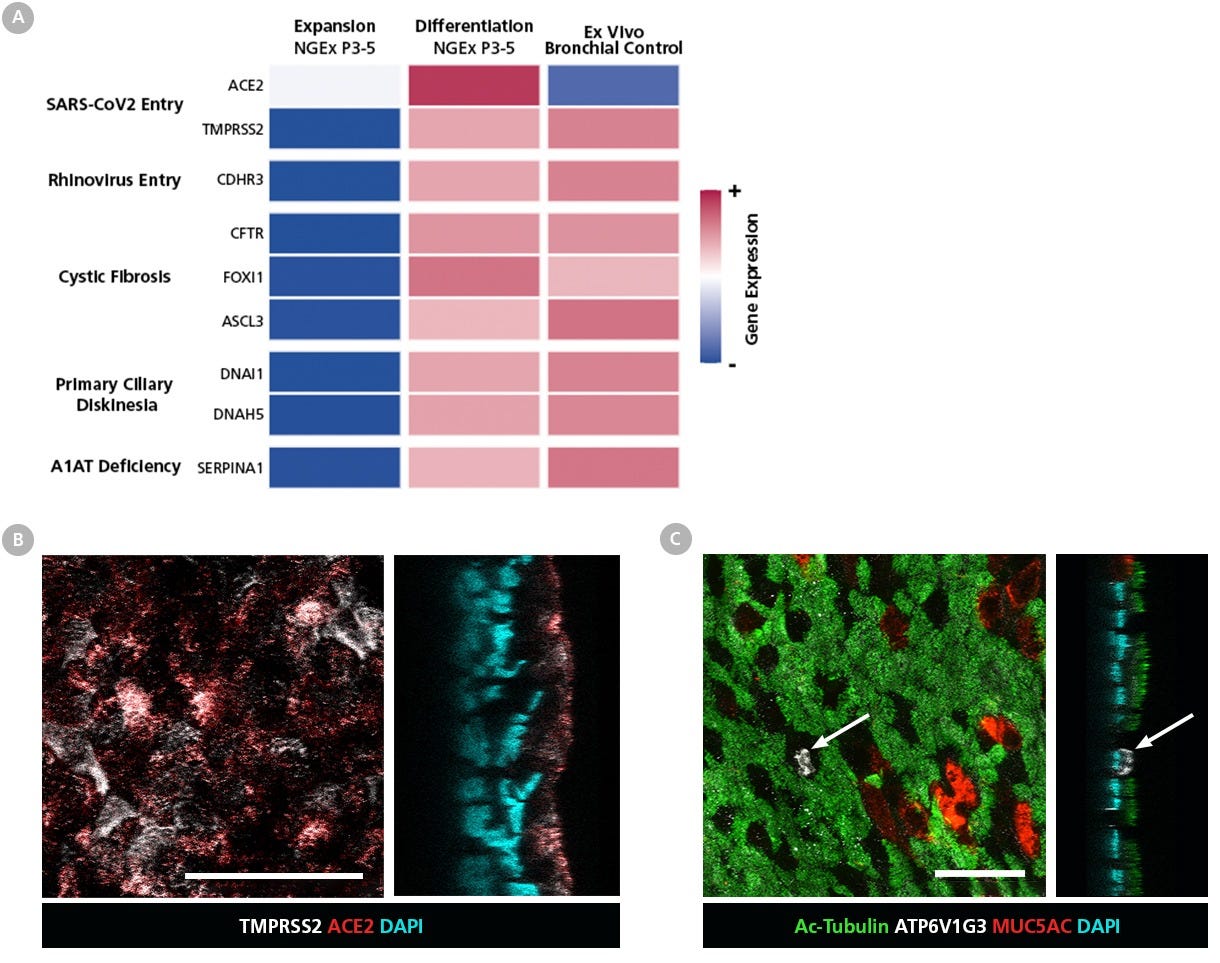
Figure 10. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Express Markers Critical for Respiratory Disease Studies After Differentiation with PneumaCult™-ALI
(A) Heatmap showing changes in the RNA levels of markers critical for respiratory disease studies during expansion of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) in PneumaCult™-NGEx (P3 - 5), and after differentiation with PneumaCult™-ALI (Catalog #05001), compared to a non-cultured ex vivo bronchial epithelial cell control (Cordero et al., 2022). The heatmap shows increased gene expression, indicating successful differentiation and physiological similarity to the ex vivo control. Columns represent the mean of 2 - 5 donors analyzed by bulk RNA-seq, with gene expression values scaled by row. After expansion in PneumaCult™-NGEx (P7 - 9) and differentiation with PneumaCult™-ALI, immunofluorescent staining shows the presence of (B) SARS-CoV-2 entry markers ACE2 (red) and TMPRSS2 (white), as well as (C) ionocyte marker ATP6V1G3 (arrows; white) within the differentiated epithelium. These results demonstrate that human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx express key respiratory disease markers and are physiologically relevant for advanced disease modeling. Scale bar = 50 µm.
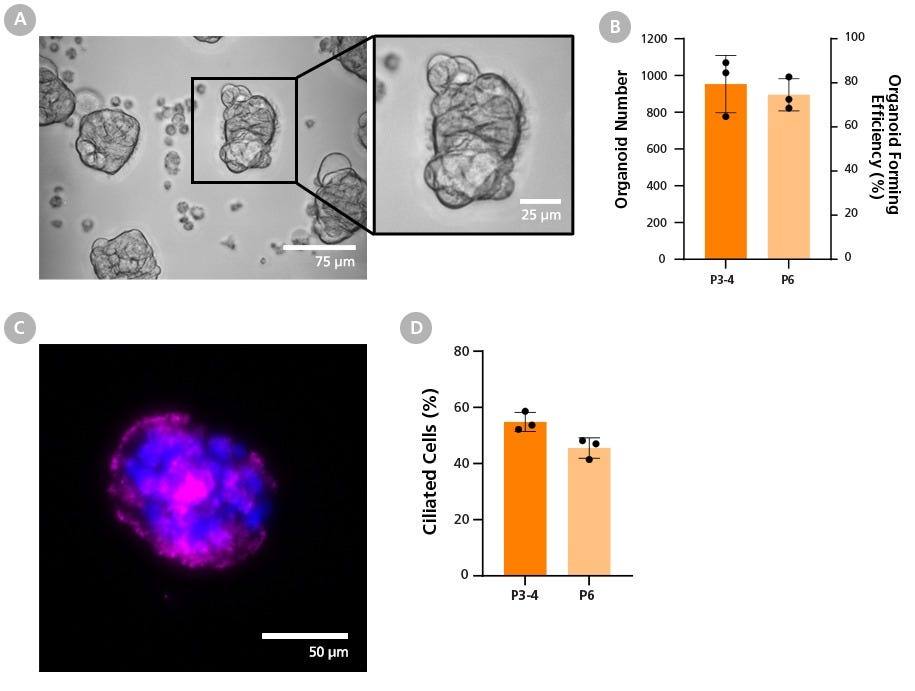
Figure 11. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Are Compatible with Apical-Out Airway Organoid Differentiation Workflows
Apical-out airway organoids were generated by seeding human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx into Aggrewell™ plates (Catalog #34415), and differentiating them using PneumaCult™ Apical-Out Airway Organoid Medium (Catalog #100-0620).
(A) Bright-field images of passage 4 organoids show ciliated cells facing outward, indicating the inversion of epithelial polarity. Scale bar = 75 µm, Inset scale bar = 25 µm.
(B) Graph showing the number of generated organoids and forming efficiency expressed as the percentage of apical-out airway organoids, at early (P3 - 4) and late passage (P6), relative to the 1,200 available microwells per Aggrewell™ plate.
(C) Immunostaining confirms the presence of ciliated cells at passage 4, as indicated by acetylated tubulin (magenta). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 75 µm.
(D) Graph showing ciliated cell percentage of apical-out organoids at early and late passage. These results confirm that HBECs expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx efficiently differentiate into apical-out airway organoids with functional cell types maintained throughout long-term culture. Data represents mean ± SD, n = 3 donors.
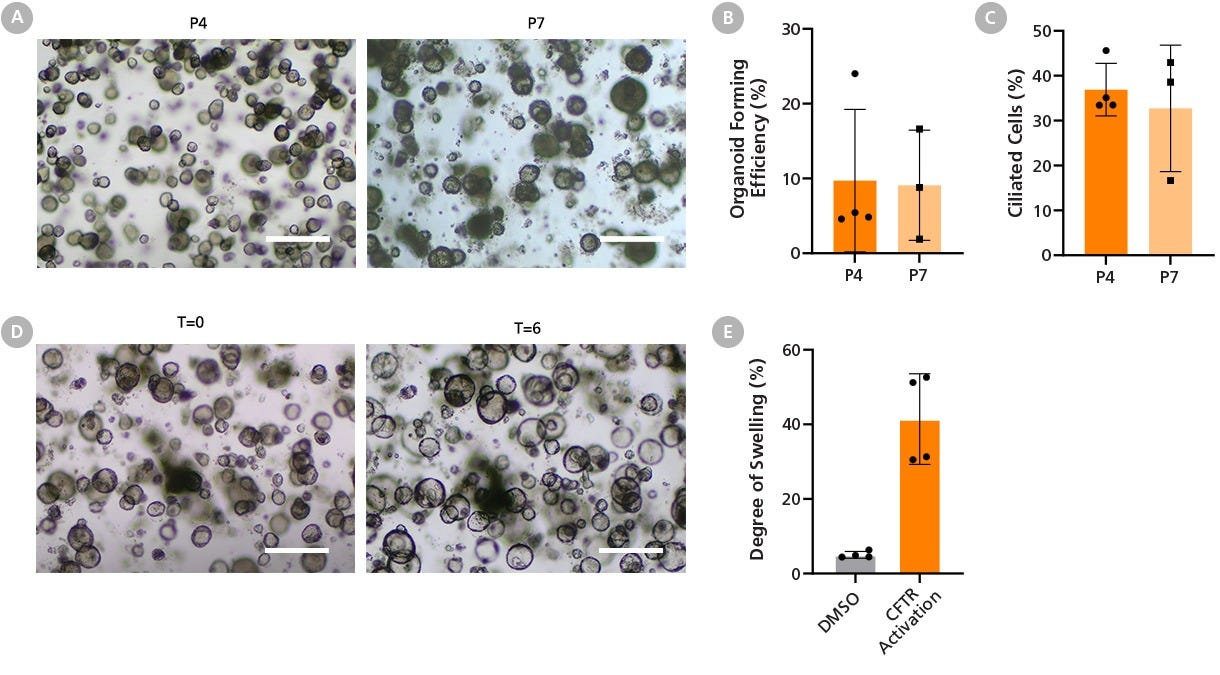
Figure 12. HBECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Are Compatible with Airway Organoid Differentiation Workflows and Support Functional CFTR Assessment
(A) Bright-field images of passage 4 (P4) and 7 (P7) apical-in airway organoids, generated from human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx and differentiated using the PneumaCult™ Airway Organoid Kit (Catalog #05060) show a consistent spheroid morphology.
(B) Organoid forming efficiency (OFE) and (C) ciliated cell percentage remain stable between early (P4) and late (P7) passages with no significant differences observed.
(D) Bright-field images of P4 PneumaCult™-NGEx-derived airway organoids were taken before (T = 0) and after 6 hours (T = 6) of treatment with Amiloride, Forskolin, and Genistein. This treatment activates ion channels, such as the CFTR chloride channel, causing chloride and water influx into the organoid lumen, allowing them to swell.
(E) After 6 hours, CFTR-activated airway organoids increased in size by over 40% compared to the DMSO vehicle control, confirming functional CFTR protein expression. Scale bar = 500 µm. Data represents mean ± SD, n = 3 - 4 donors.
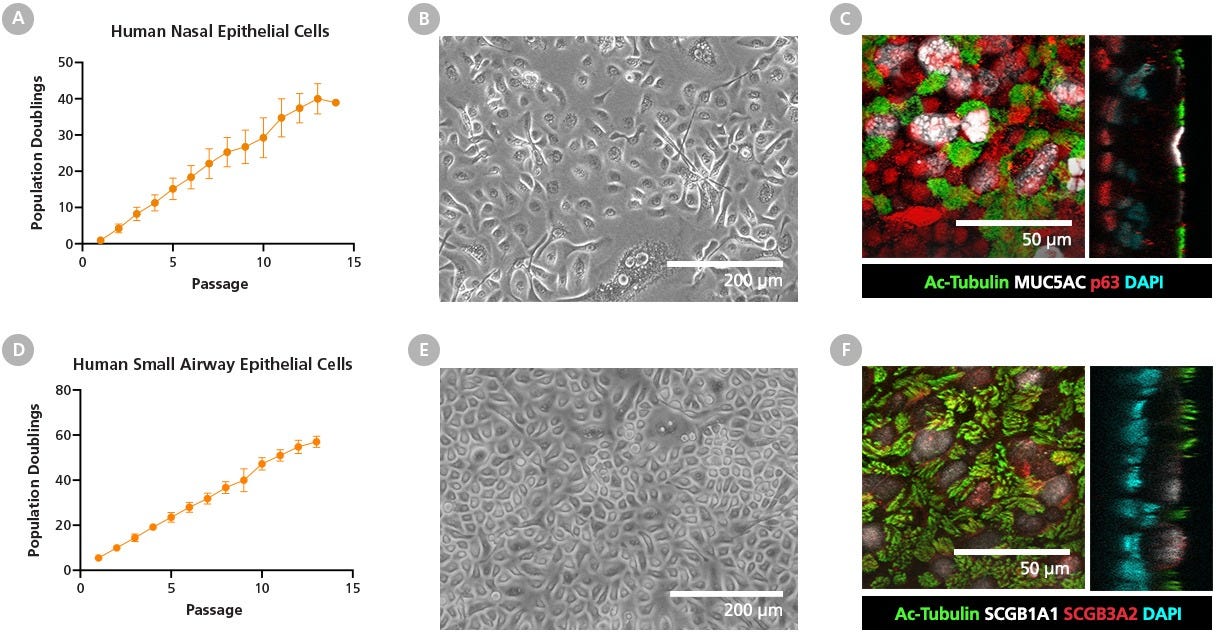
Figure 13. PneumaCult™-NGEx Enables Robust Expansion of Human Nasal and Small Airway Epithelial Cells
(A - C) Freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells (HNECs) from nasal brushings and (D - F) cryopreserved human small airway epithelial cells (HSAECs) were expanded and passaged in PneumaCult™-NGEx. Population doublings for (A) HNECs and (D) HSAECs show robust and steady expansion rates, with cells reaching up to 40 and 60 population doublings, respectively, over the course of culture. These results confirm the ability of PneumaCult™-NGEx to efficiently support long-term expansion. Data represents mean ± SD, n = 3 - 5 donors. Bright-field images of passage 2 (B) HNECs and (E) HSAECs cultured in PneumaCult™-NGEx reveal characteristic epithelial morphology, with cells forming a homogenous monolayer with a cobblestone-like appearance. Scale bar = 200 µm. (C) Immunofluorescence-stained passage 4 HNEC cultures indicate presence of differentiated cell markers normally found in the human nasal epithelium, such as ciliated (Ac-Tubulin; green) and secretory goblet cells (MUC5AC; white). Appropriate localization of basal cells along the basolateral side was visualized by immunofluorescence staining and orthogonal imaging using the basal cell markers p63 (red). Scale bar = 50 µm. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of passage 4 HSAECs confirms the presence of ciliated cells (Ac-Tubulin; green), club cells (SCGB1A1; white), and secretory cells (SCGB3A2; red) typically present in the small airways. These results collectively demonstrate that PneumaCult™-NGEx enables efficient expansion and differentiation of human small airway and nasal epithelial cells, maintaining characteristic epithelial morphology and marker expression for key small airway and nasal cell types, and ensuring their functionality through robust differentiation. Scale bar = 50 µm.
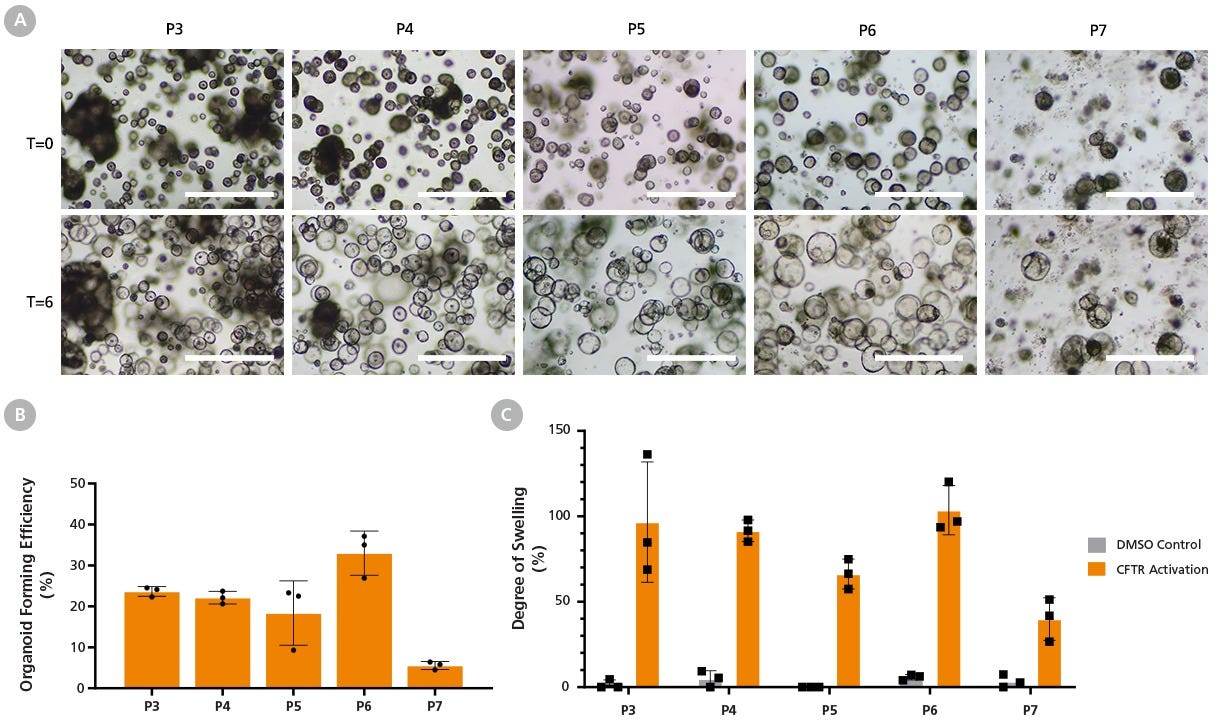
Figure 14. HNECs Expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx Demonstrate Efficient Airway Organoid Differentiation and Functional CFTR Activity After Extended Passaging
Cryopreserved, commercially available human nasal epithelial cells (HNECs) were expanded in PneumaCult™-NGEx and differentiated using the PneumaCult™ Airway Organoid Kit (Catalog #05060).
(A) HNECs were seeded at 1,500 cells per dome and imaged on Day 4 after each passage. Robust organoid formation was observed up to passage 7 (P7; top row).
(B) Organoid forming efficiency (OFE) remained stable (between 20 - 35%) throughout early and mid-passage cultures but fell below 10% after P7. This demonstrates that PneumaCult™-NGEx supports nasal organoid culture and maintains organoid formation capacity up to P6.
(A) To assess CFTR function, PneumaCult™-NGEx nasal organoid cultures were imaged before (T = 0) and 6 hours after (T = 6) treatment with amiloride, forskolin, and genistein.
(C) The degree of swelling of nasal cultures fluctuates between 70% and 100% from passage 3 - 6, before falling to approximately 40% at P7. This indicates that PneumaCult™-NGEx-derived nasal organoids exhibit a mature polarity and functional CFTR channels throughout culture up to P6. Scale bar = 1000 µm. Mean ± SD with n = 3 technical replicates, one donor.
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (9)
Related Products
-
 PneumaCult™-ALI Medium
PneumaCult™-ALI MediumSerum- and BPE-free medium for human airway epithelial cells cultured at the air-liquid interface
-
 PneumaCult™-Ex Plus Medium
PneumaCult™-Ex Plus MediumSerum- and BPE-free medium for expansion of primary human airway epithelial cells
-
 PneumaCult™-ALI-S Medium
PneumaCult™-ALI-S MediumSerum- and BPE-free medium for human small airway epithelial cells cultured at the air-liquid interface
-
 PneumaCult™ Airway Organoid Kit
PneumaCult™ Airway Organoid KitSerum- and BPE-free medium for efficient establishment and differentiation of airway organoids
-
 PneumaCult™ Apical-Out Airway Organoid Medi...
PneumaCult™ Apical-Out Airway Organoid Medi...Serum- and BPE-free medium for differentiation of human primary bronchial epithelial cells or human airway epithelial cells to mature apical-out airway organoids
-
 PneumaCult™ Alveolar Organoid Media
PneumaCult™ Alveolar Organoid MediaCell culture media for expansion and differentiation of human alveolar organoids
Item added to your cart

PneumaCult™-NGEx Medium
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.