Gene and Cell Surface Marker Expression of Pluripotent Stem Cells
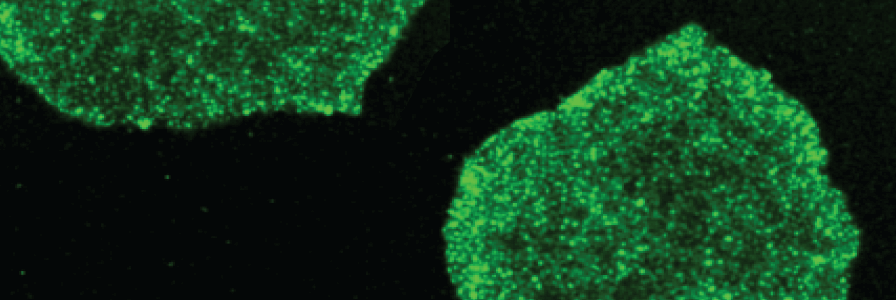
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are characterized by specific cell-surface markers, such as the glycolipid antigens SSEA3 and SSEA4, as well as the glycoprotein antigens TRA-1-60 and TRA-1-81. These antigens were initially identified on embryonic carcinoma cell lines derived from human germ cell tumors (Andrews et al., 1996) and also mark cells of the inner cell mass of pre-implantation human embryos (Henderson et al., 2002).
Transcription factors OCT3/4, SOX2, and NANOG are also highly expressed by hPSCs, and are key elements in the “pluripotency network.” They have established roles in maintaining the undifferentiated state and in generating induced pluripotent stem cells. In high-quality cultures, these cell surface and intracellular markers should be homogeneously expressed in nearly all cells.
More recently, transcriptome analyses have provided a more comprehensive view of the gene expression profile of hPSCs and allowed identification of gene signatures characterizing a spectrum of pluripotent states. New bioinformatic analyses and tools developed to understand and compare transcriptomic data will facilitate its use as a quality indicator for cell lines.
Key Publications
- The International Stem Cell Initiative reports on the characterization of 59 human embryonic stem cell lines obtained from 17 laboratories worldwide. Some variations in the expression of lineage markers were observed.
International Stem Cell Initiative et al. (2007) Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative. Nat Biotechnol 25(7): 803-16. - Andrews et al. characterized the pattern of cell surface antigen expression of cell lines derived from human germ cell tumors. The results were consistent with the previous immunohistochemical studies on tissue sections of primary germ cell tumors.
Andrews PW et al. (1996) Comparative analysis of cell surface antigens expressed by cell lines derived from human germ cell tumours. Int J Cancer 66(6): 806-16. - Henderson et al. characterized the cell surface antigen expression of the inner cell mass of human pre-implantation embryos. The results demonstrated consistent expression with human embryonic stem cells, which is unique from mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells.
Henderson JK et al. (2002) Preimplantation human embryos and embryonic stem cells show comparable expression of stage-specific embryonic antigens. Stem Cells 20(4): 329-37. - This review summarizes knowledge of the critical transcriptional networks and signaling pathways involved in hPSC self-renewal.
Huang G et al. (2015) Molecular basis of embryonic stem cell self-renewal: from signaling pathways to pluripotency network. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(9): 1741-57. - Müller et al. developed “PluriTest,” a web-based tool that allows users to compare microarray data from test samples to a database of somatic and pluripotent stem cell samples. The PluriTest algorithm determines the degree of similarity between the gene expression profile of the test sample and the database of well-characterized pluripotent stem cell lines.
Müller FJ et al. (2012) Assessment of human pluripotent stem cells with PluriTest. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
Tools for PSC Gene and Surface Marker Expression Analysis
Take the guesswork out of finding the right antibody:
- Anti-Mouse SSEA-1 (CD15) Antibody, Clone MC-480
- Anti-Mouse SSEA-3 Antibody, Clone MC-631
- Anti-Human SSEA-4 Antibody, Clone MC-813-70
- Anti-Human TRA-1-60 Antibody, Clone TRA-1-60R
- Anti-Human TRA-1-81 Antibody, Clone TRA-1-81
- Anti-Human TRA-2-49 Antibody, Clone TRA-2-49/6E
- Anti-Human TRA-2-54 Antibody, Clone TRA-2-54/2J
- Anti-Human OCT4 (OCT3) Antibody, Clone 3A2A20

